Ear defects, whether congenital or acquired due to trauma or disease, can profoundly affect an individual’s self-esteem and overall quality of life. Understanding the nuances of ear reconstruction surgery not only helps patients appreciate their options but also empowers them to make informed decisions about their health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the reasons why individuals seek this transformative procedure, detail the various surgical techniques available, and outline what patients can expect during both the process and recovery. Additionally, we will discuss potential risks, how to choose the right surgeon, and the financial aspects of ear reconstruction. We’ll also share inspiring success stories and look ahead at innovative techniques shaping the future of this field. Whether you’re considering surgery for yourself or a loved one, this post aims to provide valuable insights into restoring both appearance and function.
Understanding Ear Reconstruction Surgery
Ear reconstruction is a specialized surgical procedure aimed at restoring the appearance and function of the ear. This intricate process is especially relevant for individuals who have experienced congenital ear deformities, traumatic injuries, or significant ear loss due to medical conditions. Knowledge of the intricacies surrounding this surgery can enhance patient understanding, thereby aiding informed decision-making.
Key Concepts of Ear Reconstruction
Below is a detailed overview of essential aspects involved in this surgical field:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The primary goal is to restore the ear’s shape and restore functionality, which might include improvement in hearing abilities if applicable. |
| Candidates | Candidates include individuals with microtia (underdeveloped ear), prominent ears, traumatic ear loss, or post-tumor reconstructions. |
| Techniques | Depending on the specific needs of the patient, different techniques may be employed, including autologous reconstruction (using the patient’s tissue) or prosthetic methods. |
| Timing | The timing of the procedure can vary widely. For children with congenital issues, the ideal age for surgery is generally before school starts, whereas adults may seek this for aesthetic reasons or after injury. |
Importance of a Personalized Approach
Understanding that each patient’s anatomy and needs are unique is crucial. Surgeons tailor their approach based on various factors such as age, overall health, and specific conditions. Technological advancements have refined these methods, allowing for more personalized and less invasive options. Innovations in 3D modeling and printing are being integrated into surgical planning, improving outcomes and precision.
Psychological Benefits
Apart from the physical benefits, this procedure can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. Many patients report increased confidence, social integration, and satisfaction with their appearance following their treatment. Careful consideration of both aesthetic goals and functional restoration helps ensure that the results align with patient expectations.
Comprehensive Consultation
Before opting for any reconstructive procedure, patients should engage in an in-depth consultation with a qualified specialist. This consultation will typically encompass:
- Medical history review: Understanding previous surgeries or medical conditions.
- Physical examination: Analyzing the ear structure and overall facial symmetry.
- Discussion of goals: Detailing the patient’s desired outcomes and how they envision improvement.
- Education on techniques: Explaining various surgical options and what each entails.
Being well-informed minimizes uncertainty surrounding the surgery. Prospective patients should ask questions, clarify doubts, and explore various avenues to understand the full scope of the options available to them.
In summary, ear reconstruction is a multifaceted process that necessitates both surgical expertise and a comprehensive approach to patient care, addressing both physical needs and psychological well-being. It marks a significant step towards enhancing the lives of individuals seeking improved ear functionality and aesthetics.
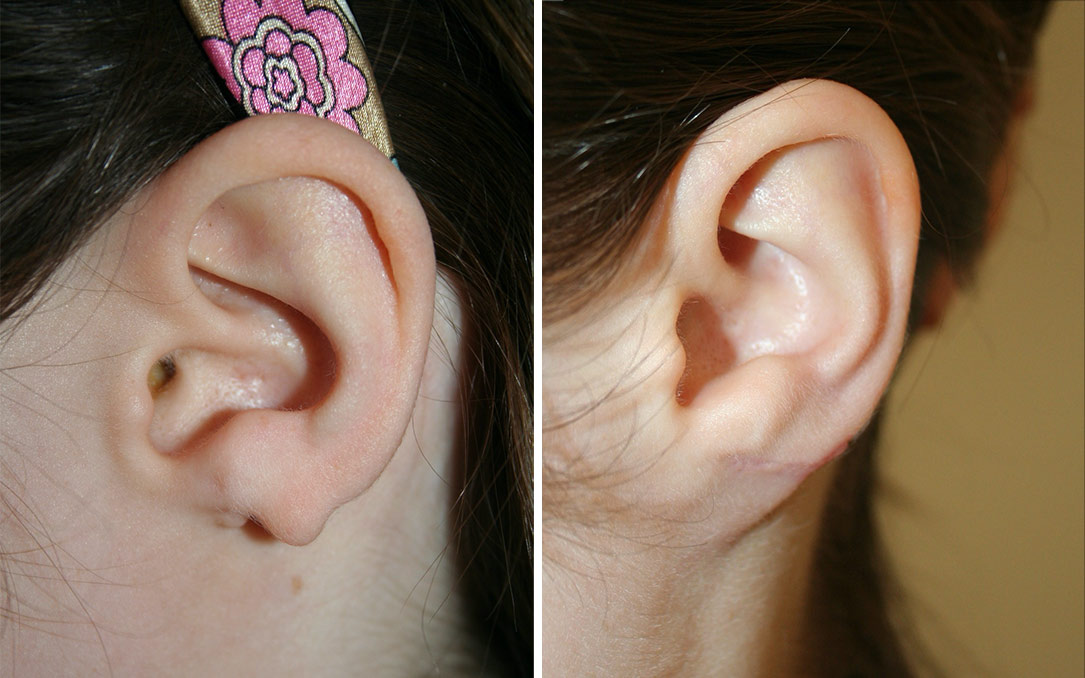
Reasons for Seeking Ear Reconstruction
Ear reconstruction surgery is often sought by individuals for various emotional, psychological, and physical reasons. Understanding these motivations can help potential patients identify their own needs and concerns regarding the procedure. Here’s a detailed look at some of the primary reasons patients opt for ear reconstruction surgery.
1. Congenital Defects
Many individuals are born with ear deformities or conditions such as microtia, where the outer ear is underdeveloped or absent. This congenital issue can lead to significant self-esteem challenges and social anxieties during childhood and adolescence. Ear reconstruction can help restore a more typical ear appearance and enhance confidence.
2. Trauma or Injury
Accidental injuries, such as those sustained from sports, accidents, or violence, can result in significant ear damage. In these situations, individuals may seek ear reconstruction to repair the external structure and regain their usual appearance. Post-trauma reconstruction can also restore functionality, such as hearing if the injury has impacted the internal structures.
3. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can necessitate the need for ear reconstruction. For example, skin cancers or infections that affect the ear may result in deformities due to surgical removal or severe scarring. Reconstruction allows patients to address both aesthetic and functional concerns by restoring an ear that may have been compromised by disease.
4. Aesthetic Preferences
Some individuals seek ear reconstruction purely for cosmetic reasons. This includes those with prominent ears (commonly known as “bat ears”) or other ear shapes that do not align with personal or societal beauty ideals. Adjusting the shape and size of the ear can significantly improve one’s self-image and interpersonal interactions.
5. Psychological Impact
Aesthetic issues related to the ears often extend beyond physical appearance to invoke emotional distress. The feeling of self-consciousness about one’s appearance can lead to anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal. By undergoing ear reconstruction, many patients experience notable improvements in their psychological well-being, as they feel more comfortable in social situations.
Summary Table of Reasons for Seeking Ear Reconstruction Surgery
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Congenital Defects | Conditions like microtia that affect ear development, leading to a desire for restoration for improved self-esteem. |
| Trauma or Injury | Damage from accidents requiring surgical intervention to restore appearance and function. |
| Medical Conditions | Loss of ear structure due to surgery for skin cancer or severe infections necessitating reconstruction. |
| Aesthetic Preferences | Patients desiring modifications for prominent or irregular ear shapes for cosmetic improvement. |
| Psychological Impact | Addressing the emotional distress related to ear aesthetics, improving overall mental health and confidence. |
6. Personal or Cultural Reasons
For some individuals, cultural expectations or personal beliefs may also play a role in the decision to undergo ear reconstruction. In societies where ear shape is tied to identity, the pressure to conform can drive individuals to seek surgical options.
In summary, the reasons for pursuing ear reconstruction surgery are varied and deeply personal. Whether motivated by congenital issues, trauma, health concerns, aesthetic preferences, or psychological factors, these motivations highlight the profound impact that successful ear reconstruction can have on an individual’s life. Understanding these reasons can help potential patients make informed decisions and prepare for their surgical journeys.
Types of Ear Reconstruction Procedures
Ear reconstruction surgery encompasses a variety of techniques tailored to address different conditions and aesthetic concerns related to the ear. Each method aims to restore not only the ear’s external appearance but also its functional capabilities. Understanding the specific types of procedures available can help patients make informed decisions regarding their treatment options.
Microtia Repair
Microtia, a congenital condition characterized by the underdevelopment or absence of the outer ear, is one of the primary reasons people seek ear reconstruction surgery. The repair process typically involves:
- Stage One: Creation of the ear structure, usually using cartilage grafts harvested from the patient’s rib cage. This cartilage is shaped to mimic the natural ear and is inserted under the skin.
- Stage Two: After a healing period, the outer skin is pulled over the new cartilage framework to form a realistic ear appearance. This often includes refining the shape and adding details for a natural look.
This multi-stage approach offers patients enhanced auditory function as well as improved aesthetics.
Otoplasty
Otoplasty, or prominent ear surgery, is designed for individuals with protruding ears or ears that lack proper shape. This procedure can be performed on children as young as five years old but is also increasingly common among adults. It involves:
- Incision Technique: Strategically placing incisions on the back of the ear to access and reshaping the cartilage.
- Ear Placement: The ear is pulled closer to the head, and any excess cartilage is removed or folded to achieve a more natural look.
Otoplasty results can be dramatic, significantly improving the ear’s positioning and overall facial symmetry.
Auricular Reconstruction Following Trauma
Individuals who have suffered ear injuries from accidents or sports may require auricular reconstruction. This procedure is often customized based on the extent of the damage and includes:
- Rebuilding using Flaps: Utilizing local flaps to reconstruct the ear’s architecture while preserving its natural contours.
- Implantation techniques: In cases where significant tissue loss has occurred, prosthetic implants can be used to create an aesthetically pleasing and functional ear.
Trauma reconstruction focuses on restoring both the appearance of the ear and its protective functions, aiding in hearing and balance.
Congenital Ear Abnormalities
Conditions such as anotia (the absence of the ear) and various syndromic ear anomalies present unique challenges. Procedures for these cases may involve:
- Composite graft techniques: Using tissue from other parts of the body to craft a new ear.
- 3D Printing: Emerging technologies now include producing custom implants tailored to each patient’s anatomical needs.
These innovations ensure each reconstruction maintains harmony with the patient’s overall facial structure.
Comparison of Techniques
| Procedure Type | Best For | Stages Involved | Duration of Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microtia Repair | Individuals with microtia | 2-3 stages | Permanent after healing |
| Otoplasty | Prominent ears | 1 stage | Long-lasting, often permanent |
| Auricular Reconstruction | Trauma recovery or severe ear deformities | 1-2 stages depending on severity | Depends on extent of reconstruction |
| Congenital Ear Abnormalities | Anotia and other congenital ear anomalies | Varies significantly based on condition | Varies significantly |
In conclusion, the choice of ear reconstruction technique is highly individualized, and it hinges on the specific conditions being addressed. Consulting with a qualified surgeon is essential to develop a personalized plan that ensures optimal results tailored to your unique needs. Each of these procedures represents a significant stride in restoring both functional and aesthetic aspects of the ear, significantly improving patients’ self-esteem and quality of life.
What to Expect During Recovery
Recovering from ear reconstruction surgery is a critical phase, requiring attention to detail and adherence to your surgeon’s advice. Understanding the recovery process can greatly alleviate concerns and help in achieving satisfactory results. Here’s what patients can generally expect during their recovery journey:
Initial Recovery Phase (Days 1-7)
The first week following your surgery is essential. Patients are typically advised to stay home and limit physical activity. During this period, expect some swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which are all normal responses to surgery. The use of ice packs on the affected area can help soothe swelling and pain.
| Recovery Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Swelling and Bruising | Noticeable swelling and some bruising are common; use ice packs intermittently. |
| Pain Management | Take prescribed medications or over-the-counter pain relievers as directed. |
| Activity Level | Rest is crucial; avoid strenuous activities including heavy lifting or exercise. |
Tips to Enhance Recovery
- Sleep Position: Avoid sleeping on the side of the surgery for at least a few weeks. Utilize pillows to keep your head elevated.
- Hygiene: Clean the surgical site gently with soap and water, but avoid soaking it in water until fully healed.
- Monitoring for Issues: Watch for signs of infection such as increased redness, prolonged swelling, or discharge. If any of these occur, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Mid-Recovery Phase (Weeks 2-4)
As you progress into your recovery, many patients notice an improvement in swelling and discomfort. However, complete healing can take time, sometimes up to 6 months, depending on individual factors.
| Recovery Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Follow-Up Appointments | Attend follow-up check-ups for monitoring healing and addressing concerns. |
| Gradual Activity Increase | Slowly reintroduce light activities; consult with your surgeon on when to resume normal activities. |
| Scar Care | Follow your surgeon’s recommendations for scar care products and techniques. |
Long-Term Considerations (Months 1-6)
After the initial healing phase, it’s essential to be patient. Full recovery can continue for months as the surgical site continues to heal and the final aesthetics become apparent.
| Recovery Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Adjustment Period | Your body may take time to adapt to the changes; it’s a gradual process. |
| Ongoing Care | Continue caring for the ear and watching any changes; be proactive in follow-up visits. |
| Emotional Adjustment | Emotional effects may surface; consider counseling or support groups if needed. |
Possible Challenges
Each patient’s experience with recovery from ear reconstruction surgery may differ. Challenges such as prolonged swelling or changes to hearing functionality can occur. Hence, staying in close contact with your care team and addressing concerns promptly is crucial in fostering a smooth recovery process.
By staying informed about what to expect and engaging actively in your recovery, you can ensure the best possible outcomes from your surgery. Patience, proper self-care, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare providers are essential elements for a successful recovery journey.
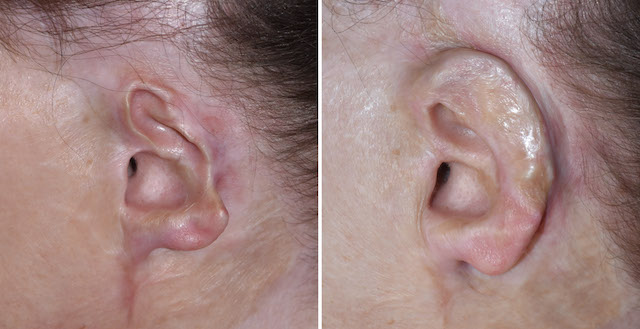
Potential Risks and Complications
While ear reconstruction surgery is a relatively safe procedure that helps many individuals regain both the aesthetic and functional aspects of their ears, it is important to recognize that all surgical interventions carry inherent risks. Understanding these potential complications can help patients make informed decisions and prepare adequately for the surgical journey.
Common Risks Associated with Ear Reconstruction Surgery
- Infection
Infection is a possibility with any surgical procedure, and ear reconstruction is no exception. Post-operative care is critical to mitigate this risk. If signs such as persistent redness, swelling, fever, or discharge from the surgical site occur, it is essential to contact the healthcare provider promptly. In most cases, infections can be treated effectively with antibiotics. - Bleeding
Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery can occur. In most cases, this is controlled during the procedure, but occasionally, patients may notice increased swelling or blood accumulation around the surgical site post-operation, known as a hematoma. Monitoring and, if necessary, treatments can prevent further complications. - Scarring and Tissue Texture Changes
Scarring is a natural part of the healing process. Patients should expect some degree of scarring from the surgery, but its visibility can vary widely among individuals. Some may experience changes in skin texture or sensitivity around the surgical site, possibly affecting the final aesthetic result. Discussing potential scarring with the surgeon beforehand can help set realistic expectations. - Asymmetry and Aesthetic Discrepancies
In some cases, the reconstructed ear may not perfectly match the natural ear in terms of size, shape, or position. While surgeons strive for symmetry, slight variations are common. Future revisions may be needed to achieve desired results. - Nerve Injury
Though rare, there is a potential for nerve injury during ear reconstruction surgery. This can lead to sensation loss or movement issues in the ear or surrounding areas. Surgeons take great care during the operation to avoid nerve pathways, but patients should be cognizant of this risk. - Prolonged Healing Time or Complications
Some individuals may experience delayed healing, which can increase the risk of other complications such as infection or improper healing. Engaging in follow-up appointments and following post-operative care instructions is crucial for promoting optimal recovery.
Important Considerations for Risk Management
Here are some key factors to consider that can help in minimizing risks:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgeon’s Experience | Opt for a surgeon who specializes in ear reconstruction and has a proven track record. Their expertise can significantly reduce the risk of complications. |
| Patient Health History | Disclose any medical conditions, allergies, or medications to the surgeon. Pre-existing conditions can affect surgical outcomes. |
| Post-Operative Care | Following all post-operative instructions, including care for the surgical site and attending follow-up appointments, can immensely reduce risks. |
| Realistic Expectations | Setting realistic goals and expectations regarding the aesthetic outcome is crucial. Discuss anticipated results with the surgeon to avoid disappointment. |
Understanding the potential risks and complications associated with ear reconstruction surgery empowers patients to take proactive measures for a smoother surgical experience. Always consult with your healthcare provider to discuss these risks in detail and create a tailored approach that suits your individual needs.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Selecting the right surgeon for ear reconstruction surgery is a crucial step that significantly influences the outcome of the procedure. With advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, it’s essential to find a qualified professional who not only possesses the necessary skills but also understands your specific needs and circumstances. Below are key factors to consider when choosing your surgeon.
Credentials and Experience
First and foremost, ensure that the surgeon you are considering is board-certified in plastic or reconstructive surgery. Board certification indicates that the surgeon has met rigorous educational and professional standards. Here are essential credentials to look for:
- Medical Degree: Confirm that the surgeon has a medical degree from a reputable institution.
- Residency: Look for surgeons who have completed a residency in plastic or reconstructive surgery.
- Fellowship: A fellowship specific to ear reconstruction or related fields can be a significant asset.
| Credential Type | Importance |
|---|---|
| Board Certification | Validation of qualifications |
| Medical School | Foundation of medical knowledge |
| Residency | Specialized training in surgery |
| Fellowship | Advanced training in a focused area |
Specialization in Ear Reconstruction
Not all plastic surgeons have the same level of expertise in ear reconstruction procedures. It is advisable to choose a surgeon who specializes in otoplasty and related reconstructions. A specialist will have a deeper understanding of the anatomy, aesthetics, and functional aspects involved in ear reconstruction, which can significantly enhance surgical results.
Review Surgical Outcomes
Ask potential surgeons about their experience with ear reconstruction and request before-and-after photographs of previous patients. Reviewing these images can give you a realistic idea of the potential outcome. Inquire about the number of procedures they perform annually, as higher volumes usually correlate with better skills and results.
Patient Reviews and Testimonials
Patient reviews are a valuable resource in assessing the surgeon’s reputation. Look for testimonials that discuss not only the surgical outcomes but also the overall patient experience, including the following aspects:
- Communication: How effectively did the surgeon communicate the surgical plan and expected outcomes?
- Aftercare: What kind of post-operative care and support were provided?
- Satisfaction: How satisfied were previous patients with their results?
Consultations and Comfort Level
Schedule consultations with multiple surgeons to gauge your comfort level with each one. During these meetings:
- Ask Questions: Inquire about the techniques they use, recovery time, and potential risks.
- Assess the Environment: Evaluate the surgical facility’s cleanliness and whether it is accredited.
- Gauge Interpersonal Skills: A good surgeon not only possesses technical skills but also demonstrates empathy, patience, and a willingness to address your concerns.
Cost and Insurance
Finally, discussing the cost of ear reconstruction surgery and what your insurance may cover is vital. Some insurers may cover ear reconstruction if it’s deemed medically necessary, so ensure to verify with your insurance provider.
Overall, choosing the right surgeon involves doing thorough research, asking informed questions, and feeling confident in your decision. A well-selected surgeon can make a world of difference in not just the functional aspect but also in restoring confidence and quality of life for individuals seeking ear reconstruction.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
When it comes to ear reconstruction surgery, understanding the financial implications is as crucial as the medical aspects. The costs associated with this intricate procedure can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of reconstruction needed, geographical location, the surgeon’s expertise, and the facility’s reputation. Consequently, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what to expect financially, as well as the potential for insurance coverage.
Understanding the Costs
The overall cost of ear reconstruction can be divided into different components. Below is a table highlighting the main cost factors involved:
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgeon’s Fee | The fee charged by the surgeon performing the operation, which may vary based on expertise and experience. |
| Anesthesia Fee | This includes the cost of anesthetic agents and the anesthesiologist’s services during surgery. |
| Facility Fees | Charges for using the surgical facility, including operating rooms and recovery areas. |
| Pre-operative Testing | Costs associated with necessary tests before surgery, such as blood work and imaging. |
| Post-operative Care | Follow-up appointments and any medications needed for recovery are included here. |
| Additional Procedures | Some patients may require additional procedures, such as grafts or adjustments, which can increase overall costs. |
Insurance Coverage Considerations
In many cases, health insurance can help alleviate some of the financial burdens associated with ear reconstruction surgery. However, coverage varies significantly based on the insurer and the specific policy. Here are some key points to keep in mind regarding insurance:
- Medical Necessity: Insurance companies are more likely to cover the costs if the surgery is deemed medically necessary rather than purely cosmetic. Conditions that cause disfigurement, congenital deformities, or trauma-related issues typically qualify for coverage.
- Pre-authorization: Most insurers require pre-authorization for surgical procedures. This means you’ll need to submit documentation, including medical records and the surgeon’s recommendations, to demonstrate the necessity of the procedure.
- In-Network vs. Out-of-Network: The choice of surgeon and facility can greatly influence the amount covered. Opting for an in-network provider generally results in lower out-of-pocket expenses due to arranged pricing agreements with insurers.
- Deductibles and Copays: It’s essential to understand your policy’s deductible, which is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. Additionally, be aware of any copays that will apply for surgical procedures and follow-up visits.
Financial Options for Patients
Understanding the costs and insurance coverage is important; however, there are also financial options available for patients who may face significant out-of-pocket expenses. Consider the following:
- Payment Plans: Many clinics provide flexible financing options or payment plans to help manage costs over time, making it more feasible for patients to proceed with surgery.
- Medical Loans: Specialized medical lending institutions offer loans specifically for procedures, allowing patients to cover costs upfront and pay back the loan in installments.
- Healthcare Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you have a health savings account, you can use these funds to cover qualified medical expenses, which can be an excellent way to reduce the overall financial burden.
In summary, while ear reconstruction surgery can represent a substantial investment, understanding the various costs involved and the potential for insurance coverage alongside available financial options can empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their health and wellbeing.
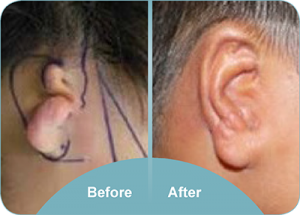
Patient Success Stories
The field of ear reconstruction surgery has seen remarkable advancements, and the testimonials from patients who have undergone these procedures underscore the transformative effects on both their appearance and quality of life. Here, we share inspiring success stories of individuals who sought to restore their ears through surgical intervention. These narratives not only highlight the technical success of the procedures but also resonate with the emotional and social impacts that follow.
Transformative Journey of Emma
Emma, a 32-year-old woman, was born with a congenital ear deformity known as microtia, which left her with a significantly underdeveloped ear on one side. For years, she faced challenges in social settings, often feeling self-conscious about her appearance. After thorough research and consultations, Emma decided to undergo ear reconstruction surgery, which involved the construction of a new ear using her rib cartilage.
- Before Surgery: Emma felt anxious during interactions and avoided activities like swimming or attending social events.
- Post-Surgery Experience: The results of her surgery were dramatic. Not only did she gain a fully formed ear, but her confidence surged. Emma described feeling liberated from the insecurities that had previously overshadowed her life.
With the visible changes came a sense of normalcy; she enjoyed her first beach trip in years without the fear of judgment and even began modeling, an activity she had always dreamed of pursuing.
An Inspiring Outcome for Ryan
Ryan, a 25-year-old male, suffered significant damage to his ear due to a traumatic accident during a sports activity. The loss of his external ear affected both his hearing and self-esteem. After consulting a specialist, Ryan opted for a more complex ear reconstruction procedure that not only restored the aesthetic structure of his ear but also enhanced its function.
Surgical Details:
- Type of Procedure: Autologous ear reconstruction using rib cartilage.
- Recovery Time: Six weeks for initial healing, followed by gradual resumption of activities.
Post-surgery, Ryan noted a remarkable increase in auditory function, allowing him to engage in conversations more naturally. He also stepped back into sports with improved self-image, saying, “I feel like I’ve gotten my life back!” This positive change in mindset played a crucial role in his overall recovery and reintegration into his social circles.
Joyful Resolution for Sarah
Sarah, a 40-year-old professional, faced the repercussions of otoplasty done in her youth, which resulted in asymmetry and dissatisfaction with her ears. After years of consideration, she opted for a correctional ear reconstruction surgery, which aimed to refine the shape and size of her ears while ensuring they were symmetrically aligned.
Lovely Aspects of Her Journey:
- Sarah shared her fears about undergoing yet another surgery but emphasized how the expertise of her surgeon alleviated her concerns.
- Following her surgery, she not only admired her new look in the mirror but received compliments from friends and colleagues, which boosted her morale.
Her success story highlights the significance of seeking professional help when previous procedures don’t yield the desired outcomes.
The Impact of Community and Support
These patient stories resonate far beyond individual transformations. The emotional and physical benefits of ear reconstruction surgery are profound, influencing not only the patients but their families and friendships as well.
In a supportive community environment, individuals who undergo such surgeries can share experiences and encouragement, forming bonds that further facilitate healing. Whether it’s participating in local support groups or online forums, the journey to recovery and acceptance often includes the strength derived from shared experiences.
The triumphs of Emma, Ryan, and Sarah exemplify the improvements that ear reconstruction surgery can bring, highlighting its enduring impact on personal confidence, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
Future Innovations in Ear Reconstruction Techniques
The field of ear reconstruction is undergoing significant advancements driven by technological innovations and a deeper understanding of anatomical complexities. These developments promise not only improved surgical techniques but also enhanced outcomes for patients seeking to restore both the appearance and function of their ears. Below, we explore some of the exciting innovations on the horizon that are shaping the future of ear reconstruction surgery.
Regenerative Medicine
One of the most promising areas in ear reconstruction is regenerative medicine. Researchers are working on utilizing stem cells and tissue engineering to create new ear structures from a patient’s own cells. This not only minimizes the risk of rejection but also has the potential to offer more natural-looking results. Moreover, ongoing studies are exploring how to optimize cartilage growth in laboratories, potentially eliminating the need for the traditional cartilage grafts harvested from other parts of the body.
Custom 3D Printing
3D printing technology is revolutionizing many areas of medicine, and ear reconstruction is no exception. Surgeons are now able to create customized ear prototypes tailored specifically to the unique anatomical features of individual patients. This innovation allows for precise fitting and a more natural aesthetic. Here’s how the 3D printing process enhances ear reconstruction:
| Innovation | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Customized Models | Allows for individualized solutions, reducing surgical errors |
| Material Variety | Offers the possibility of using biocompatible materials that integrate with human tissue |
| Surgical Accuracy | Improves the precision of the surgical resection and reconstruction, enhancing overall outcomes |
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques are set to change the landscape of ear reconstruction. By reducing the size of incisions, surgeons can decrease healing time and minimize scarring. Endoscopic techniques, where small cameras are used to guide the surgery, allow for greater precision and a quicker recovery, making it a preferred choice among modern surgeons.
Enhanced Imaging Techniques
The use of advanced imaging technologies like 3D CT scans and MRI has revolutionized pre-operative planning and intraoperative guidance. Surgeons can visualize the anatomy in unprecedented detail before making incisions, tailoring surgical plans to the individual patient’s anatomy. This level of detail aids in achieving superior results and minimizes complications.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is starting to play a role in various medical fields, including ear reconstruction. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of surgical data to predict outcomes, optimize surgical plans, and even assist in real-time decision-making during procedures. This technological leap could significantly enhance surgical precision and patient safety.
Biodegradable Scaffolds
Developing biodegradable scaffolds for tissue reconstruction offers another innovative approach. These scaffolds can provide structural support for new tissue growth and gradually dissolve as natural tissue replaces them. This method not only enhances healing but also reduces the potential complications associated with permanent implants.
Conclusion
As we look ahead, the future of ear reconstruction surgery seems promising, brimming with innovations that aim to improve cosmetic and functional results for patients. Each of these advancements—from regenerative medicine to the utilization of AI—will ultimately contribute to streamlined processes, enhanced safety, and improved outcomes. As these pioneering techniques continue to evolve, patients can anticipate even higher standards of care in their journey toward ear restoration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ear reconstruction surgery and who is it for?
Ear reconstruction surgery is a surgical procedure designed to restore the shape and appearance of the ears, which may have been affected by congenital conditions, trauma, or diseases such as cancer. This type of surgery is often recommended for individuals who have either missing or deformed ears, including those born with microtia (a condition where the outer ear is underdeveloped). The goal is to improve both the aesthetic appearance and the functional capacity of the ear, enhancing the individual’s self-esteem and quality of life.
What are the different techniques used in ear reconstruction surgery?
There are several techniques used in ear reconstruction surgery, including autologous reconstruction, where cartilage from the patient’s own body (usually the rib) is used to create the ear framework. Another method is the use of prosthetic ears, which are custom-made and can provide a natural appearance without surgery. Additionally, some surgeons utilize tissue expansion techniques to create new ear tissue before sculpting the ear’s shape. The choice of technique depends on various factors such as the extent of reconstruction needed, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences.
What is the recovery process like after ear reconstruction surgery?
The recovery process after ear reconstruction surgery varies depending on the complexity of the procedure and the individual’s response to surgery. Typically, patients can expect some swelling and discomfort, which can be managed with pain medications prescribed by the surgeon. Most patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities for at least a few weeks to allow proper healing. Follow-up appointments are essential during the recovery period to monitor healing and remove any stitches if necessary. Full recovery may take several weeks, during which time the final aesthetic results will gradually become evident.
Are there any risks or complications associated with ear reconstruction surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, ear reconstruction surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include bleeding, infection, scarring, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. Additionally, there could be a possibility of unsatisfactory aesthetic results, necessitating further surgery. It is crucial for patients to discuss these risks with their surgeon during the consultation process to ensure they have realistic expectations and to weigh the benefits against the potential complications.
How can I prepare for ear reconstruction surgery?
Preparing for ear reconstruction surgery involves several steps. First, it’s important to have thorough consultations with your surgeon, during which you should discuss your goals, medical history, and any concerns. Your surgeon may request certain medical tests to assess your health. It is recommended to avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption in the weeks leading up to the surgery, as these can affect healing. Also, arranging for a caregiver or someone to assist you post-surgery can facilitate a smoother recovery process.