In a world that increasingly values physical appearance and self-confidence, many men find themselves grappling with the challenges posed by excess breast tissue. This condition, known as gynecomastia, can significantly impact one’s self-esteem and body image. Understanding this issue extends beyond mere aesthetics; it involves recognizing the underlying causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. Whether you are seeking non-surgical methods or considering surgical interventions, this comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the essential knowledge to make informed decisions. Join us as we explore the journey from diagnosis to recovery and learn how to maintain a chest that reflects your identity and confidence.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. This condition can affect one or both breasts and may lead to varying degrees of discomfort or self-consciousness. It is essential to distinguish this condition from pseudogynecomastia, which is primarily caused by excess fatty tissue rather than glandular tissue. Understanding the nuances between these conditions is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
The underlying mechanism behind gynecomastia involves an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels in the body. While estrogen is typically associated with female characteristics, it is also present in males, albeit in lower concentrations. In cases where testosterone levels drop or estrogen levels rise, the result can be the overdevelopment of breast tissue.
Key Characteristics of Gynecomastia:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Age of Onset | Can occur at any age but is most common during puberty, in middle age, or in older men. |
| Physical Symptoms | Enlargement of breast tissue, which might feel firm or rubbery; potential sensitivity or tenderness in the breast area. |
| Bilateral vs. Unilateral | May manifest as enlargement in one breast (unilateral) or both (bilateral). |
| Associated Conditions | Can be linked to hormonal disorders, certain medications, obesity, or chronic diseases. |
Gynecomastia can affect self-esteem and body image significantly, leading to psychological distress. Furthermore, males experiencing this condition may avoid social situations, physical activities, or wearing fitted clothing due to embarrassment. Understanding the impact on mental health is essential in addressing the condition holistically.
Prevalence:
Research indicates that gynecomastia occurs in approximately 40–60% of men at some point in their lives. While the condition can be a transient phenomenon—especially during puberty—it can also be persistent. Those who experience it during puberty often find that breast tissue may reduce on its own after a couple of years; however, for others, particularly those in later age groups, the condition may continue without intervention.
Hormonal Factors:
Several factors can lead to hormonal imbalances, which precipitate the development of enlarged breast tissue. These include:
- Aging: Testosterone levels tend to decrease with age, while body fat increases, resulting in higher estrogen levels.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some heart medications, can contribute to hormonal changes.
- Health Conditions: Disorders such as Klinefelter syndrome, hyperthyroidism, or liver disease can influence hormone levels, leading to gynecomastia.
In summary, gynecomastia is a complex condition that encompasses physical, emotional, and hormonal dimensions. Understanding these elements can help individuals identify the condition early and seek appropriate evaluation and treatment options. Males experiencing symptoms or related concerns should consult healthcare professionals who can guide them through the intricacies of the diagnosis and potential avenues for treatment. By fostering awareness about ogynaecomastia, we can reduce stigma and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
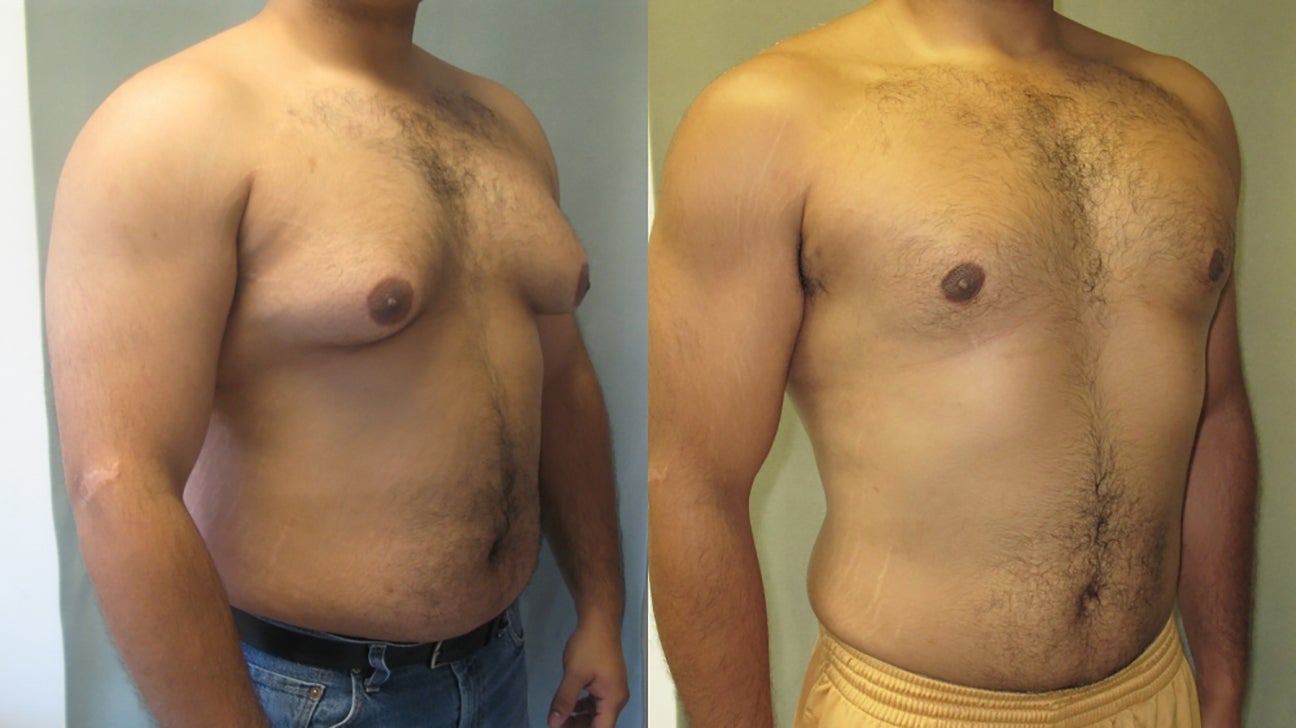
Causes of Gynecomastia
Understanding what contributes to the development of excessive breast tissue in males is crucial for anyone seeking to address this condition effectively. Several factors can lead to the development of gynecomastia, and these influences can vary significantly depending on individual circumstances. Below, we explore some of the primary causes, categorized for easy comprehension.
| Category | Causes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Imbalance | Testosterone and Estrogen Imbalance | An increased level of estrogen and a decreased level of testosterone can promote breast tissue growth. This is particularly common during puberty or aging. |
| Medical Conditions | Liver and Kidney Diseases | Illnesses that affect the liver or kidneys can impair hormone metabolism, resulting in hormonal imbalances that may lead to gynecomastia. |
| Hyperthyroidism | An overactive thyroid can elevate estrogen levels, leading to breast tissue development. | |
| Tumors | Hormonal-producing tumors, especially those in the testes or adrenal glands, can stimulate breast tissue growth. | |
| Klinefelter Syndrome | This genetic disorder involves an extra X chromosome in males, leading to lower testosterone levels and potential breast development. | |
| Medications | Certain Prescription Drugs | Various medications such as anti-androgens (used for prostate cancer), anabolic steroids, and some antidepressants can influence hormone levels and contribute to gynecomastia. |
| Illicit Drug Use | Substances like marijuana and heroin can disrupt hormonal balance, contributing to breast tissue growth in males. | |
| Lifestyle Factors | Obesity | Excess fat can lead to increased estrogen production. Adipose tissue can convert androgens to estrogen, potentially leading to breast tissue accumulation. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Heavy drinking can cause liver damage, thus impairing hormone metabolism and increasing estrogen levels. | |
| Anabolic Steroids | The introduction of synthetic testosterone or other anabolic substances can lead to hormonal changes that promote gynecomastia. |
Hormonal Imbalance: A Core Factor
The cornerstone of gynecomastia’s development lies in hormonal imbalance, where the interplay between testosterone and estrogen becomes disrupted. In males, testosterone generally regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics. When estrogen levels rise disproportionately—whether due to natural life stages like puberty and aging, or external factors—it can result in breast tissue proliferation. This imbalance can often trigger noticeable changes during adolescence, a critical period for hormonal development.
Medical Conditions and Their Impacts
Certain medical conditions exacerbate hormonal imbalance, thereby fostering the conditions necessary for the growth of unwanted tissue. Liver diseases, for instance, can hinder the body’s ability to metabolize hormones effectively, and weakened kidney functionality can also contribute to the buildup of hormones that promote gynecomastia. Other conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, not only elevate metabolic rates but can also lead to an overall hormonal imbalance that sometimes results in gynecomastia.
Medication and Substance Influence
Both prescribed and recreational substances have been linked to changes in hormonal levels. For instance, medications aimed at managing prostate cancer can block male hormones while promoting breast development. Moreover, the use of anabolic steroids, often abused for muscle gain, can adversely swing hormonal levels, emphasizing the need for caution among users.
Lifestyle Choices
Lastly, lifestyle choices play a significant role. Obesity remains a key contributor, as increased body fat can facilitate higher estrogen production. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, which diminishes hormone regulation. These choices can combine with the aforementioned factors, culminating in a pronounced development of breast tissue.
By understanding these diverse causes, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their health and seek appropriate interventions.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For many individuals dealing with excess tissue that results in a feminine chest appearance, exploring non-surgical treatment options can be an effective first step. These alternatives can help address the condition without the need for invasive surgical procedures. Here are some of the most commonly recommended non-surgical options:
1. Medications
Certain medications can assist in managing hormone levels and reducing breast tissue. For instance, anti-estrogens, such as tamoxifen, may be prescribed to inhibit estrogen’s activity in the body. Meanwhile, aromatase inhibitors, like anastrozole, work by preventing the conversion of androgens into estrogens. It’s crucial to remember that these treatments may not be effective for all individuals, and results can vary based on the underlying causes of the condition.
2. Hormone Therapy
Hormonal imbalances are often at the root of this condition. In cases where low testosterone levels contribute to the development of excessive breast tissue, hormone therapy might be recommended. This treatment involves supplementing testosterone to restore normal levels in the body. Monitoring is vital during this process to avoid complications associated with hormone replacement.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly influence the condition. These changes may include:
- Dietary Modifications: Incorporating a balanced diet can help manage weight and hormone levels. Foods rich in zinc and vitamin D can be particularly beneficial for testosterone production.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can effectively reduce body fat, promote muscle development, and help enhance the appearance of the chest area.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce excess fatty tissue in the chest. For some individuals, weight loss may alleviate the appearance of the condition.
4. Compression Garments
Wearing specific compression garments may provide immediate aesthetics benefits. These garments help flatten the chest area and are often made from materials that offer support without restricting movement. It’s important to choose the right fit to ensure comfort and effectiveness.
5. Natural Remedies
Some individuals explore natural remedies to manage symptoms. Herbal supplements like ginseng, fenugreek, and turmeric are thought to have balancing effects on hormone levels. However, it’s crucial to approach these remedies with caution and consult a healthcare professional before trying any new supplement, as efficacy can vary, and interactions with medications may occur.
Summary of Non-Surgical Treatment Options
| Treatment Type | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Anti-estrogens and aromatase inhibitors | Varies per individual |
| Hormone Therapy | Testosterone supplementation | Effective for hormonal imbalances |
| Lifestyle Changes | Diet, exercise, and weight management | Helpful in many cases |
| Compression Garments | Restorative clothing that flattens the chest area | Temporary solution |
| Natural Remedies | Herbal options for hormone balancing | Limited success potential |
By exploring these non-surgical options, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing excessive chest tissue. Consultation with healthcare professionals is recommended to tailor treatment based on personal circumstances. Ultimately, addressing this condition should focus on individual needs and preferences, leading to a more confident self-image and improved quality of life.
Surgical Procedures for Gynecomastia
Surgical intervention is often considered when non-surgical options for addressing excess tissue are ineffective. Surgical procedures aimed at correcting gynecomastia are tailored according to the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient. They not only help to restore a more masculine chest aesthetic but also provide lasting results that can significantly improve an individual’s self-esteem. Here’s a detailed look into the surgical options available.
Types of Surgical Procedures
There are several surgical techniques used to address excess breast tissue, each with its unique approach and benefits. The primary procedures include:
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Liposuction | A minimally invasive method that removes fat deposits from the breast area using a cannula. | Less invasive, minimal scarring, shorter recovery. |
| Mastectomy | A more invasive procedure that involves the removal of glandular breast tissue. | Effective for severe cases, long-lasting results. |
| Combination Surgery | A hybrid approach using both liposuction and mastectomy to address different tissue types. | Comprehensive treatment for varying tissue types. |
Liposuction
Liposuction for the treatment of gynecomastia is ideal for patients primarily dealing with excess fatty tissue. During the procedure, small incisions are made around the nipple or in the armpit area to minimize visible scarring. A cannula is inserted to suction out fat cells, resulting in a more contoured and masculine chest.
Advantages of Liposuction:
- Less invasive than mastectomy, resulting in a shorter recovery time.
- Minimal scarring, as the incisions are relatively small.
- Patients can typically return to normal activities within a week.
Mastectomy
Mastectomy is generally advised when there is significant glandular tissue. This procedure removes both the fatty and glandular breast tissue. Surgeons may perform a periareolar incision, which encircles the areola to reduce visibility of scars.
Advantages of Mastectomy:
- Provides significant and permanent results in cases of moderate to severe gynecomastia.
- Reduces the amount of breast tissue drastically, yielding a flatter, firmer appearance.
- Suitable for those who have not achieved desired results with non-surgical treatments.
Combination Surgery
When individuals present with a mix of fatty and glandular tissue, a combination procedure may be the best course of action. This entails a tailored approach where both liposuction and mastectomy are performed to achieve optimal results.
Advantages of Combination Surgery:
- Allows for a more customized treatment plan based on individual tissue composition.
- Maximizes the benefits of both surgical methods to create an aesthetically pleasing contour.
- Addresses a broader range of gynecomastia severity.
Choosing the Right Procedure
Choosing the appropriate surgical procedure requires a thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Factors influencing this decision include:
- Severity of Gynecomastia: Mild cases may benefit from liposuction, while moderate to severe cases may necessitate mastectomy.
- Body Composition: Understanding the distribution of fat and glandular tissue helps in tailoring the approach.
- Personal Goals: A patient’s desired outcome should align with the recommended surgical method, taking into account the potential risks and benefits.
Surgical treatment of gynecomastia is a significant step for many individuals seeking to improve their body image and regain confidence. With the right surgical approach, patients can look forward to achieving a flatter, more contoured chest that aligns with their desired masculine physique.
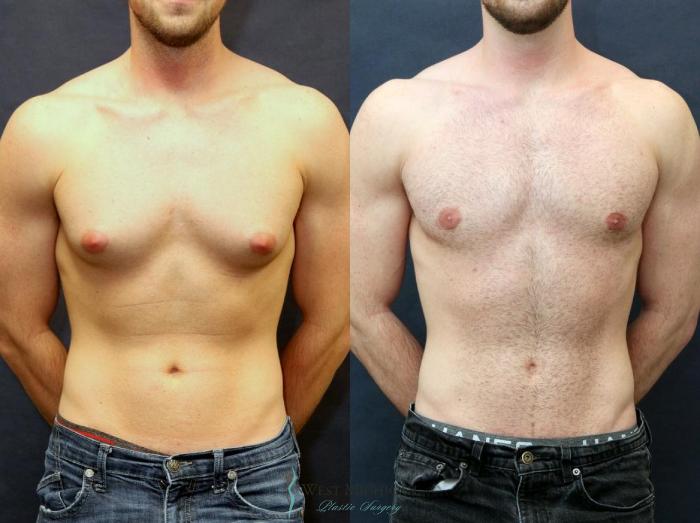
Recovery Process After Treatment
The recovery process after treatment for excess tissue in the chest area is a critical phase that determines not only the effectiveness of the procedure but also the overall experience of the individual. A clear understanding of what to expect during this time can significantly aid in a smoother recovery and ensure optimal results.
Immediate Post-operative Care
Following surgical intervention, patients will typically be monitored in a recovery area for several hours. Pain management is a primary focus during the first few days post-surgery. Here are some essential aspects of immediate post-operative care:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Pain Management | Prescription of pain relievers to minimize discomfort; over-the-counter options may be recommended as needed. |
| Dressings and Bandages | Application of a surgical compression garment to facilitate healing and reduce swelling. |
| Activity Limitations | Rest is advised for the initial 48 to 72 hours; light movements can help improve circulation. |
First Week After Surgery
The first week is often marked by swelling, bruising, and some discomfort. Implementing the following strategies can facilitate healing:
- Ice Application: Ice packs can be applied to the chest area to manage swelling. Aim for 20 minutes of icing followed by a 20-minute break, particularly during the first 48 hours.
- Elevation: Keeping the upper body elevated while resting can help reduce swelling. Use pillows to achieve a comfortable angle while sleeping or resting.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Two weeks post-surgery, a follow-up visit with the surgeon will evaluate the surgical site and ensure proper healing. Any concerns or unexpected symptoms should be communicated during this visit.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle modifications during the recovery process can greatly enhance healing:
| Adjustments | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Physical Activity | Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for at least four weeks to prevent stress on the chest area. |
| Hydration and Nutrition | Maintain proper hydration and consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and proteins to promote tissue repair. |
| Smoking and Alcohol | It’s recommended to refrain from smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can impede healing. |
Long-term Recovery
The full recovery timeline typically ranges from six weeks to several months, depending on the individual’s health and the extent of the procedure. However, several indicators can signify a smoother recovery:
- Decreased Discomfort: By the end of the first week, a notable decrease in pain should occur.
- Reduction of Swelling: By weeks two to four, swelling and bruising should significantly decrease, revealing initial results.
- Return to Routine: Gradual increments of activity can resume as healing progresses, which may include resuming lightweight workouts and low-impact cardio exercises.
- Monitoring Changes: Finally, participants should remain vigilant for any unusual changes or complications such as persistent pain, fever, or unusual discharge, which would warrant immediate consultation with a healthcare provider.
Emotional and Psychological Adjustment
Recovery isn’t solely physical. The psychological aspect cannot be overlooked. Newfound confidence can significantly boost self-esteem but may require an adjustment period. Engaging in supportive networks, whether personal or professional, can provide necessary emotional guidance during this transition.
Overall, a focus on a well-structured recovery process encourages individuals to embrace their journey towards achieving a masculine chest post-treatment. The combination of careful management during healing and adjustments in daily life plays an integral role in the overall success of the procedure.
Tips for Maintaining a Masculine Chest
Achieving a masculine chest following treatment for excess tissue is only the beginning; maintaining this desired physique requires ongoing effort and dedication. With a focus on lifestyle, exercise, and nutrition, anyone looking to sustain a toned chest can implement practical strategies. The following tips will help ensure that efforts to reduce excess tissue yield long-lasting results.
Embrace Regular Exercise
Consistency in a comprehensive workout regimen is vital for muscle development. Here are effective exercises that can help:
| Exercise | Focus Area | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Bench Press | Chest, shoulders | 2-3 times per week |
| Push-Ups | Chest, arms | 3-4 times per week |
| Dumbbell Flyes | Chest | 2-3 times per week |
| Chest Dips | Lower chest, triceps | 2-3 times per week |
| Cable Crossovers | Upper chest | 2-3 times per week |
Incorporating these exercises can enhance muscle definition and maintain the contour of the chest. Moreover, combining strength training with cardiovascular exercises promotes overall fat loss and aids in maintaining a lean physique.
Adopt a Balanced Diet
An essential aspect of maintaining a masculine chest involves following a healthy eating plan. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, one can support muscle maintenance and overall health. Here’s what to consider:
- Protein-Rich Foods: Lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products promote muscle growth and repair.
- Healthy Fats: Opt for unsaturated fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which support hormonal balance.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide energy for workouts and essential vitamins and minerals.
Sample Daily Meal Plan:
| Meal | Example Food |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-grain toast |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with berries |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing |
| Snack | Hummus with carrot sticks |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with quinoa and asparagus |
Stay Hydrated
Hydration plays a crucial role in muscle recovery and overall wellness. Water aids in nutrient transport, metabolic processes, and exercise performance. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day supports optimal body function and helps maintain the desired physique.
Focus on Posture
Maintaining good posture can significantly affect the appearance of the chest. Regularly engaging in exercises that strengthen the back and shoulders can correct posture and enhance the presentation of the chest. Simple posture corrections can include:
- Shoulder Blade Squeeze: Sit or stand straight and squeeze shoulder blades together for several seconds.
- Wall Angels: Stand against a wall and raise and lower arms in a “Y” shape while keeping contact with the wall.
Monitor Weight
Gaining or losing weight impacts the overall appearance of the chest. Regularly monitoring weight and maintaining a stable range can prevent future complications with chest appearance. If fluctuations are experienced, adjustments to diet and exercise routines should be implemented promptly.
Avoid Excessive Alcohol and Substance Use
Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding recreational substances are crucial for hormonal balance and overall health. Excessive consumption can lead to weight gain, disrupt hormone levels, and hinder muscle development.
By following these insightful strategies, anyone can successfully maintain a masculine chest. Building a routine centered on exercise, balanced nutrition, hydration, and healthy lifestyle choices not only preserves gains achieved through treatment but also enhances overall well-being.
When to Consult a Specialist
Recognizing when to seek professional help is crucial in effectively addressing the issues related to male breast tissue prominence. While many individuals may feel uncertain about whether their condition warrants a medical consultation, several key indicators can guide the decision to reach out to a specialist. Consulting a qualified healthcare provider, typically a plastic surgeon or an endocrinologist, can provide clarity and guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
Key Indicators for Consultation
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent Symptoms | Individuals experiencing ongoing breast tissue enlargement that does not respond to lifestyle changes should seek specialized care. |
| Physical Discomfort | If discomfort, tenderness, or pain becomes prevalent, it’s essential to consult a specialist to evaluate underlying causes. |
| Psychological Impact | Significant emotional distress, anxiety, or low self-esteem related to the appearance of the chest warrants professional consultation. |
| Lifestyle Changes | If weight loss, exercise, or dietary modifications have not improved the condition, a specialist can provide alternative treatment pathways. |
| Hormonal Concerns | If there are signs of hormonal imbalance, such as changes in libido or energy levels, it’s critical to consult a healthcare provider. |
| Family History | A family history of breast conditions or related concerns may increase the urgency for a professional evaluation. |
Types of Specialists to Consider
- Plastic Surgeons: They evaluate the condition and discuss potential surgical options to reduce excess tissue, tailoring the approach to the patient’s unique anatomy and aesthetic goals.
- Endocrinologists: These specialists assess hormonal issues, possibly contributing to breast tissue prominence. They focus on the body’s endocrine system, providing insight into potential treatments to address hormonal imbalances.
- Primary Care Physicians: Often the first point of contact, they can perform initial assessments, rule out other medical conditions, and refer patients to appropriate specialists.
Importance of Timely Consultation
Seeking consultation at an early stage has numerous benefits including:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Specialists can perform detailed assessments, utilizing imaging techniques when necessary to rule out other medical conditions, such as lipid aberrations or tumors.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Based on their evaluations, specialists can offer personalized approaches—ranging from lifestyle modifications to medical treatment, and if necessary, surgical procedures.
- Support and Guidance: Patients can receive emotional support and resources. Specialists are typically well-versed in the psychological aspects of the condition and can offer strategies to manage any psychological impact.
- Preventative Measures: Regular consultations, especially for those with familial concerns or hormonal imbalances, can lead to early interventions, potentially preventing future issues or complications.
Questions to Ask Your Specialist
When preparing for an appointment, consider preparing a list of questions to ask your healthcare provider, such as:
- What might the underlying cause of the breast tissue prominence be?
- Are there specific tests that you recommend to understand the condition better?
- What non-surgical and surgical treatment options do you suggest?
- How long is the recovery time for a surgical procedure?
Ultimately, early consultation with a specialist not only provides clarity but aids individuals in navigating their options efficiently while addressing their concerns regarding masculine chest appearance. Taking initiative in seeking professional expertise can lead to successful management and improved self-confidence.
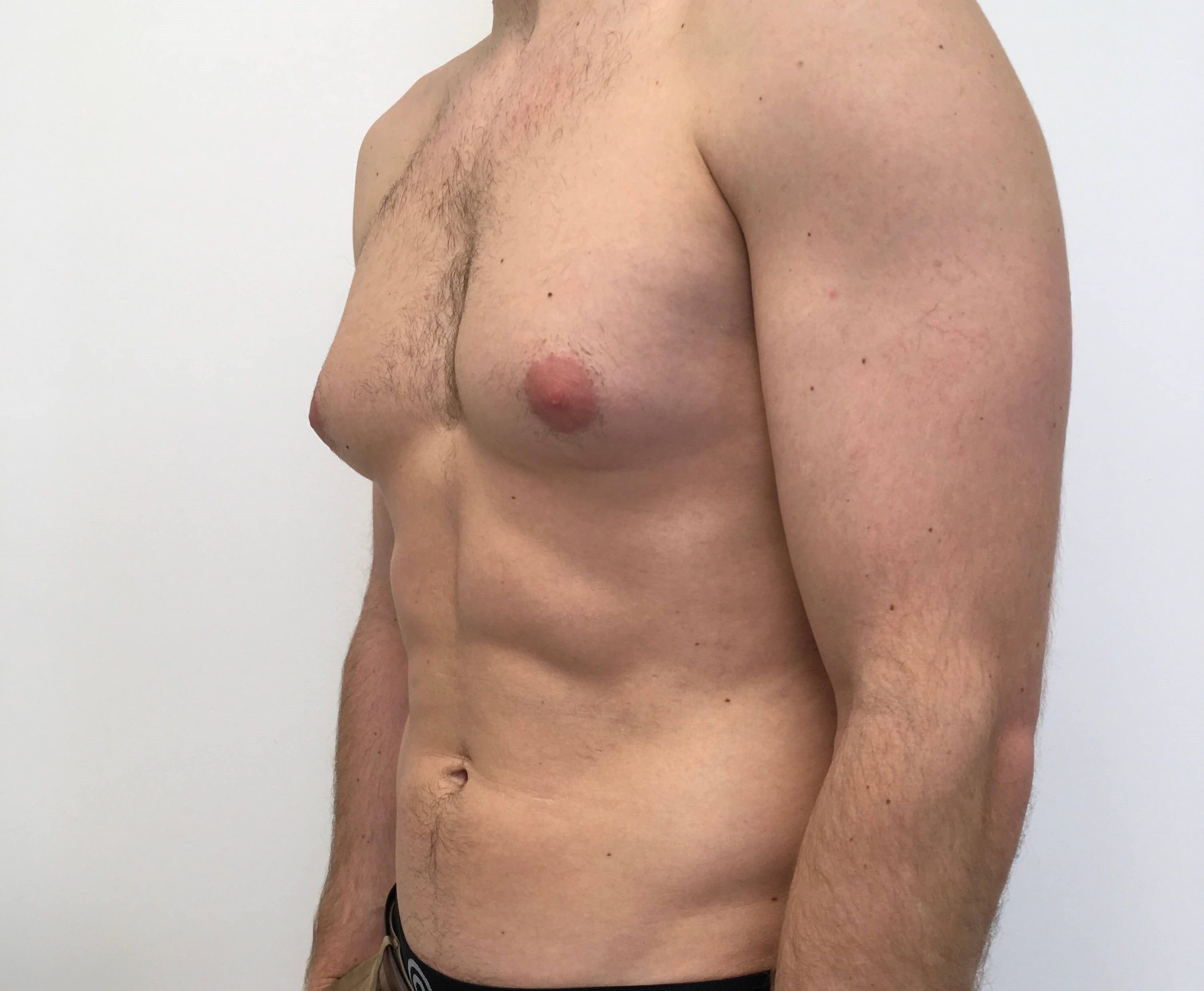
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gynecomastia and what causes it?
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. This condition can occur due to hormonal imbalances, particularly an increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone levels. Factors contributing to gynecomastia include puberty, aging, obesity, certain medications, and underlying health issues such as liver or kidney disease. Understanding the cause is essential for determining the appropriate treatment.
What are the treatment options available for gynecomastia?
Treatment options for gynecomastia vary based on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Mild cases may resolve on their own, while more severe cases may require interventions such as lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, or surgery. Surgical options include liposuction to remove excess fatty tissue or mastectomy to excise glandular tissue. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to evaluate the best course of action for each individual.
What should I expect during gynecomastia surgery?
During gynecomastia surgery, patients can expect to undergo either liposuction, gland excision, or both procedures, depending on the amount of tissue to be removed. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, and patients can usually go home the same day. Postoperative care will include wearing a compression garment to minimize swelling and pain management. Recovery time varies, but many patients return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Are there any risks associated with gynecomastia surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, gynecomastia surgery carries some risks. Potential complications include infection, bleeding, scarring, asymmetry, and changes in nipple sensation. However, when performed by a qualified surgeon, the risks are minimal, and the results can significantly improve a patient’s self-esteem and physical appearance. It’s important to discuss any concerns with the surgeon prior to the procedure.
How can I prevent gynecomastia from recurring after treatment?
Preventing the recurrence of gynecomastia involves addressing its underlying causes. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can be beneficial, as obesity often contributes to hormonal changes related to breast tissue growth. Avoiding substances that can affect hormone levels, such as anabolic steroids or certain medications, is also crucial. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor hormonal health and catch any issues early.