Navigating the complexities of body image can be challenging, especially for men dealing with male gynecomastia, a condition characterized by enlarged breasts. This blog post delves into the multifaceted aspects of gynecomastia, starting with its causes and symptoms, and shedding light on the emotional toll it can take. Furthermore, we’ll explore effective lifestyle changes, available medications, and surgical options that can help reclaim confidence and improve overall well-being. Whether you’re seeking solutions for yourself or looking to support a loved one, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about treatment and management.
Understanding Male Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in individuals assigned male at birth. This condition can cause physical discomfort and often leads to emotional distress among those it affects. Understanding this phenomenon is essential for recognizing its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
Definition and Characteristics
Gynecomastia is derived from the Greek words ‘gyne’ meaning woman and ‘mastos’ meaning breast. This clinical term refers specifically to the benign proliferation of glandular tissue in the breast, leading to an increased volume and prominence. It is important to differentiate gynecomastia from pseudogynecomastia, which is primarily caused by fat deposition without the enlargement of glandular tissue.
Characteristics of Male Gynecomastia:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Age Groups Affected | Often occurs during puberty, middle age, or later life |
| Appearance | Firm, rubbery tissue beneath the nipple area |
| Bilateral vs. Unilateral | Can occur on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) |
| Associated Symptoms | Tenderness, sensitivity, or pain in the breast area |
The Epidemiology of Gynecomastia
The prevalence of this condition varies significantly based on age and biological factors. It is estimated that about 50% to 60% of males experience gynecomastia at some point in their life, particularly during puberty due to hormonal fluctuations. The steep decline in testosterone levels typically seen in older men can also contribute significantly to the development of this condition.
Hormonal Imbalances
The underlying cause of gynecomastia often revolves around hormonal imbalances, specifically the ratio of testosterone to estrogen. As testosterone levels decrease, either naturally with age or due to other health conditions, the relative proportion of estrogen increases. This increase can stimulate breast tissue growth.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Hormonal Disorders | Conditions like hypogonadism affecting testosterone levels |
| Medications | Some such as anti-androgens and anabolic steroids |
| Health Conditions | Issues like liver disease, kidney dysfunction, or tumors |
| Substance Use | Alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroid abuse |
Psychological Impact
Beyond the physical aspects of gynecomastia, the psychological burden cannot be overlooked. Many individuals may experience embarrassment or self-consciousness, which can interfere with social activities or intimate relationships. Support systems and counseling can be crucial in aiding those affected to cope with the emotional ramifications of the condition.
In summary, understanding male gynecomastia encompasses a wide array of factors including its definition, characteristics, prevalence, causes, risk factors, and psychological implications. This foundational knowledge not only aids in recognizing the condition but also in exploring the comprehensive treatment avenues available for those affected.
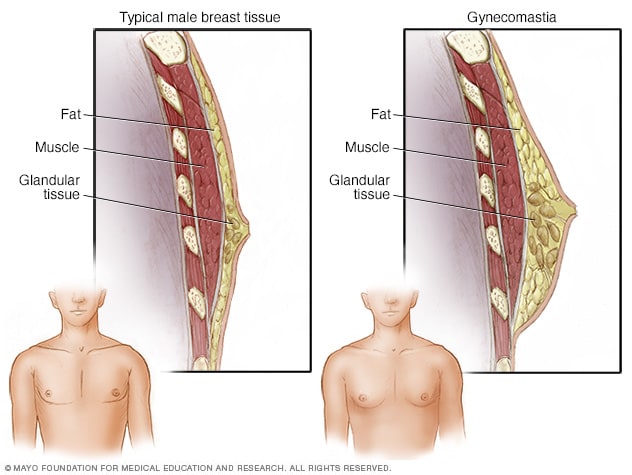
Causes of Enlarged Male Breasts
Enlarged male breasts, commonly known as gynecomastia, can stem from multiple underlying causes, each of which can significantly impact hormonal balance, body composition, and overall health. Below, we delve into the primary factors contributing to this condition, offering a comprehensive breakdown for better understanding.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Hormonal Changes | Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly an increase in estrogen or a decrease in testosterone, can lead to breast tissue enlargement. Hormonal changes are often experienced during puberty, older adulthood, or conditions that affect the endocrine system. Cancers of the testicles or adrenal glands, hyperthyroidism, and liver disease can disrupt this balance, resulting in gynecomastia. |
| Medications | Certain medications may induce gynecomastia as a side effect. Common culprits include:
|
| Genetic Factors | Genetic predispositions may also play a role in the development of gynecomastia. Hereditary conditions like Klinefelter syndrome result in abnormal chromosome patterns, ultimately causing hormonal imbalances and physical development resulting in enlarged breasts. |
| Obesity | Excess body fat can contribute to increased levels of estrogen, artificially skewing hormonal balance. Individuals with obesity may find a higher likelihood of developing enlarged breast tissue. This condition can be further aggravated by lifestyle factors, including poor diets and lack of exercise, which can perpetuate the cycle of weight gain and hormonal changes. |
| Cirrhosis and Liver Disease | Liver dysfunction often results in an imbalance of estrogen and testosterone production. The liver plays a critical role in metabolizing hormones; thus, severe liver disease or cirrhosis can lead to increased estrogen levels in the bloodstream, causing the breast gland tissue to swell. |
| Endocrine Disorders | Certain disorders, such as hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), can influence how the body uses hormones. This condition impacts hormone levels, potentially leading to the development of gynecomastia. Pheochromocytomas, tumors that produce excess catecholamines, can also cause fluctuations in hormone levels contributing to breast enlargement. |
| Age-Related Changes | Aging is a natural factor contributing to gynecomastia. As men age, testosterone levels generally decline, which can sometimes lead to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels. Consequently, older adults may experience an uptick in breast tissue growth. |
Understanding the various causes that lead to enlarged male breasts is pivotal for effective prevention and treatment strategies. Most importantly, identifying these factors with the help of a healthcare professional can provide guidance on potential lifestyle modifications or necessary medical interventions to alleviate the symptoms associated with gynecomastia. Addressing the underlying cause of this condition is often the first step toward achieving a balance in hormone levels and restoring self-confidence.
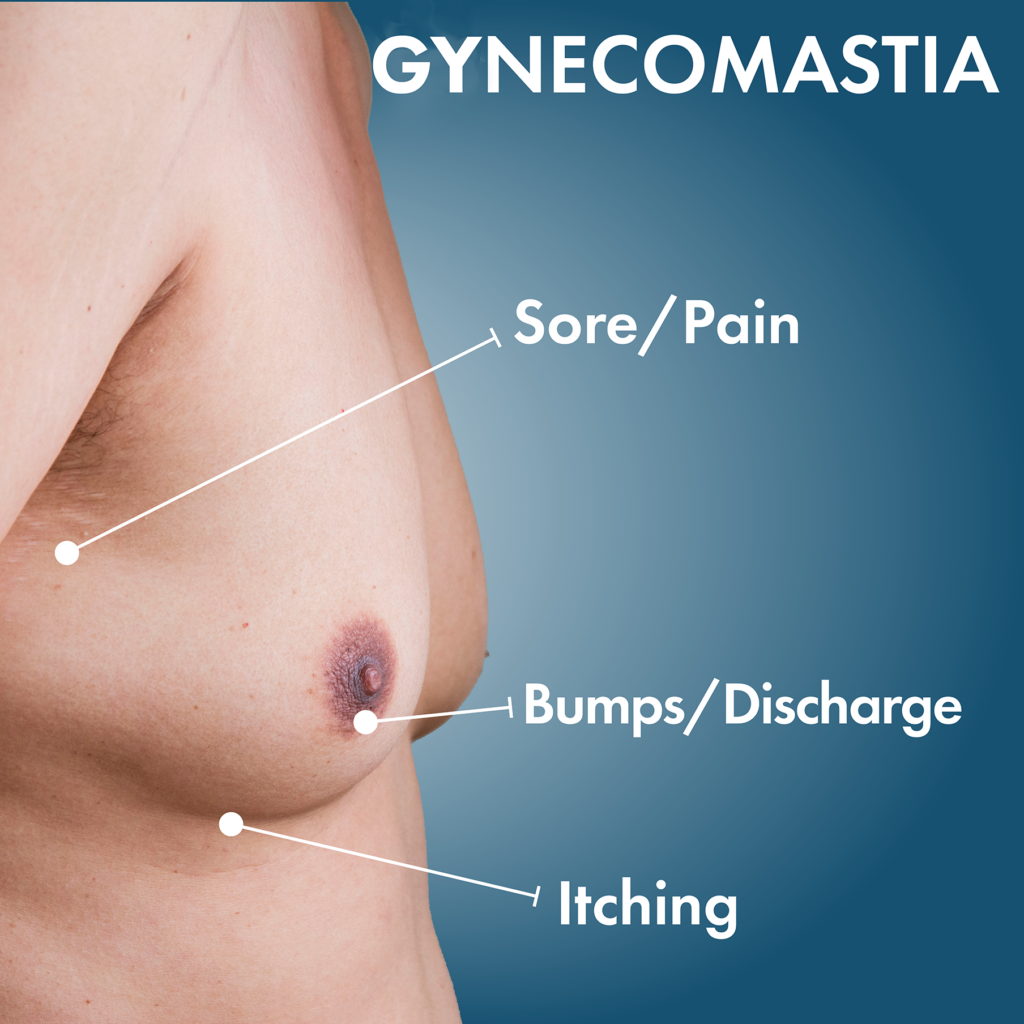
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms associated with gynecomastia is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Enlarged male breasts can manifest in several ways, and it’s important to recognize these signs early on. While many men may experience some level of breast tissue development, not all cases are indicative of gynecomastia. Below is a detailed look at the symptoms and the diagnostic process.
Common Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia typically presents a range of symptoms that can vary in severity depending on the individual. Here are some common signs:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Breast Swelling | A noticeable enlargement of chest tissue feels tender or firm to the touch. |
| Breast Tenderness | Sensitive or painful breasts when pressed or during physical activities. |
| Discomfort | General discomfort in the chest area, particularly when wearing tight clothing. |
| Nipple Changes | Changes in the appearance of the nipples, including retraction or discharge. |
| Skin Changes | Some individuals may notice skin changes around the breast area, such as rashes or unusual pigmentation. |
Many of these symptoms can be distressing, affecting self-esteem and body image. If any of these signs persist for a significant period, seeking a healthcare professional’s advice is advisable.
Diagnostic Process for Gynecomastia
Diagnosing gynecomastia involves a comprehensive assessment. Healthcare professionals typically conduct the following steps:
- Medical History: The physician will ask about your medical history, including any previous conditions, medications, or hormonal treatments you’ve undergone. They may inquire about family history related to similar symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination helps in assessing breast tissue, nipple discharge, and any other physical abnormalities. The healthcare provider will also evaluate other areas of the body to check for associated conditions.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to assess hormone levels, including testosterone and estrogen, as imbalances can contribute to breast enlargement. Additional tests may include liver and kidney function tests to rule out underlying health issues.
- Imaging Studies: In some cases, imaging studies such as mammograms or ultrasounds may be performed to differentiate between gynecomastia and other conditions, such as male breast cancer or lipomastia (fatty tissue without glandular enlargement).
- Biopsy: Rarely, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the composition of breast tissue and confirm the diagnosis. This step is generally taken only in atypical or concerning cases where there may be a suspicion of malignancy.
Understanding Diagnosis Results
It’s important to interpret the diagnostic results carefully. Here’s a comparison of common conditions that might mimic gynecomastia:
| Condition | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Gynecomastia | Firm breast tissue, often bilateral, usually not painful. |
| Pseudogynecomastia | Fatty tissue without glandular expansion; common in obesity. |
| Breast Cancer | Hard lump, may be unilateral, and could be associated with skin changes. |
| Lipidoma | Often painless, mobile fatty mass typically found under the skin. |
The distinction between these conditions is vital, as the treatment and management strategies can vary significantly. Early diagnosis can greatly enhance the effectiveness of treatment and improve outcomes for individuals dealing with gynecomastia. The next steps following a diagnosis will depend on the severity of the condition and its underlying causes, guiding the most appropriate treatment options.
The Emotional Impact of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue, is not merely a physical condition; it often carries significant emotional and psychological consequences. The emotional impact of this condition can vary widely among individuals, but many experience a range of negative feelings that affect their daily lives.
Feelings of Embarrassment and Shame
For many men, living with enlarged breasts can lead to deep-seated embarrassment and shame. This is particularly true in cultures where physical appearance is highly valued. Such feelings often prevent individuals from participating in social activities, including swimming or gym outings, where they might be exposed or required to remove their shirts. This avoidance behavior can lead to social withdrawal, ultimately exacerbating feelings of isolation and distress.
Low Self-Esteem and Body Dysmorphia
Encounters with gynecomastia can trigger low self-esteem, as men may internalize societal stereotypes about masculinity and body image. The perceived failure to meet these ideals can lead to pervasive negative thoughts about one’s body. In some instances, this dissatisfaction can evolve into body dysmorphic disorder, where individuals obsessively focus on perceived flaws and develop a distorted view of their own body.
Key Emotional Effects of Gynecomastia
| Emotional Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Embarrassment | Feelings of self-consciousness in public settings. |
| Shame | Internalized perceptions of inadequacy aligned with masculinity norms. |
| Anxiety | Increased worry about others’ perceptions and evaluations. |
| Low Self-Esteem | Persistent negative thoughts leading to feelings of worthlessness. |
| Depression | Prolonged sadness and lack of interest in activities once enjoyed. |
| Social Withdrawal | Avoidance of social situations to prevent potential humiliation. |
Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety is another common emotional consequence related to gynecomastia. Concerns regarding judgment from peers can lead to heightened stress levels. Men may find themselves preoccupied with thoughts about their appearance, which can become a source of chronic anxiety. This emotional turmoil can impact interpersonal relationships, work life, and overall mental health.
Coping Strategies
Addressing the emotional challenges associated with gynecomastia is crucial for well-being. Below are some effective coping strategies:
- Therapy: Seeking professional counseling or therapy can provide a safe space to explore feelings of shame, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in reshaping negative thought patterns.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can foster a sense of community among men experiencing similar challenges. Sharing experiences can help diminish feelings of isolation and normalize the emotional response to gynecomastia.
- Communication: Openly discussing feelings with trusted friends or family can alleviate emotional burden.
- Education: Understanding that gynecomastia is relatively common and often temporary can help reduce anxiety and feelings of isolation.
The Journey Towards Acceptance
Ultimately, accepting one’s body, regardless of conditions like gynecomastia, can be a long and challenging journey. However, it is a journey that many undertake successfully, leading to improved self-image and emotional resilience. Engaging in open dialogues about body image and seeking support can make a significant difference in managing the emotional toll of gynecomastia, enabling individuals to lead fulfilling lives despite the condition.

Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Managing the discomfort and aesthetic concerns associated with enlarged male breasts can often be effectively addressed through lifestyle changes and the implementation of home remedies. While these methods may not serve as a universal cure for gynecomastia, they can significantly alleviate symptoms and contribute to overall breast health. Below, we present a comprehensive guide detailing practical lifestyle modifications and natural remedies to support those experiencing this condition.
Dietary Adjustments
One of the fundamental aspects of managing enlarged male breasts is adopting a healthy diet. Poor dietary choices can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, leading to the development or worsening of gynecomastia. Here are some dietary changes to consider:
| Food Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lean Proteins | Supports muscle development and reduces fat accumulation – opt for chicken, turkey, and fish. |
| Healthy Fats | Avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help balance hormone levels. |
| Fruits and Vegetables | Provide necessary vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals that assist in tissue repair and overall health. |
| Whole Grains | Promote a consistent energy supply and aid in weight management. |
Physical Activity
Incorporating a consistent exercise routine can also make a considerable difference. Regular physical activity helps in maintaining a healthy body weight, which may help minimize the appearance of enlarged breasts. Consider these types of exercise:
- Strength Training: Engaging in resistance training at least two times a week can help increase muscle mass and reduce body fat. Focus on upper body exercises like bench presses, push-ups, and chest flyes.
- Cardiovascular Exercises: Activities like running, swimming, or cycling can assist in burning calories and reducing overall body fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly.
- Flexibility and Stability Workouts: Incorporating yoga or Pilates can enhance body awareness and support overall health and recovery.
Herbal Remedies
Several herbal supplements and teas are thought to support hormonal balance and overall well-being:
| Herb | Usage | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Ginger | Tea or supplement | May assist in digestion and reduce inflammation. |
| Turmeric | Spice or supplement | Contains curcumin, which may help in reducing fat. |
| Green Tea | Brewed daily | Rich in antioxidants; may support metabolism. |
| Dandelion | Tea or supplement | Believed to support liver function, which plays a role in hormone regulation. |
Stress Management
Emotional stress can influence hormonal levels, potentially contributing to breast enlargement. Engaging in stress-reducing practices can provide significant benefits:
- Mindfulness Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and guided imagery can help in relaxing the mind and body.
- Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of good quality sleep each night, as insufficient rest can lead to hormonal imbalances.
- Hobbies and Social Activities: Engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment can alleviate stress and enhance overall mental well-being.
A Note on Alcohol and Smoking
Both excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can negatively impact hormone levels, potentially worsening gynecomastia. Reducing or eliminating these factors can lead to improvements in hormonal balance and overall health.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes and home remedies can support individuals dealing with enlarged male breasts, contributing to both physical and emotional well-being. While these approaches may not replace professional medical advice or treatment, they can complement existing treatment strategies. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your lifestyle or starting new supplements, especially if existing health conditions are present.
Medications and Their Role in Treatment
The management of gynecomastia often involves a multi-faceted approach, where medications play an essential role in alleviating the symptoms and addressing the underlying causes. While not every individual with enlarged male breasts will require pharmaceutical intervention, certain cases are responsive to specific medical treatments. Understanding these medications can provide insight into their effectiveness and potential side effects.
Hormonal Medications
A common cause of gynecomastia is an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels. Hormonal medications are often utilized to restore this balance.
Table 1: Hormonal Medications for Gynecomastia
| Medication | Type | Mechanism of Action | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen | Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM) | Blocks estrogen’s effects in breast tissue | Used in moderate to severe cases |
| Raloxifene | SERM | Similar function to tamoxifen, usually for osteoporosis | Also effective in treating gynecomastia |
| Testosterone | Hormone | Counteracts low testosterone levels | Used in testosterone deficiency cases |
- Tamoxifen and Raloxifene work by selectively blocking the estrogen receptors in breast tissue, which can help in shrinking enlarged breasts. Studies indicate that these medications can effectively reduce breast tissue size in many men, especially those experiencing gynecomastia related to hormonal imbalances.
- While testosterone replacement therapy can be beneficial, it may not be suitable for every individual, particularly for those whose gynecomastia is not linked to low testosterone levels. Careful evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Another class of medications that can be effective in treating gynecomastia are aromatase inhibitors. These drugs function by reducing the conversion of androgens into estrogens, thus lowering estrogen levels in the body.
Table 2: Aromatase Inhibitors
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Anastrozole | Inhibits aromatase production | Often used in postmenopausal women, can apply to men with certain conditions |
| Letrozole | Blocks estrogen synthesis | Used for hormone-sensitive conditions |
- Anastrozole and letrozole are examples of aromatase inhibitors. Though they are primarily used in hormone-sensitive breast cancer treatment, they have shown promise in managing cases of gynecomastia by normalizing estrogen levels.
Considerations and Side Effects
While medications can be efficient in treating gynecomastia, they are not without potential side effects. Users might experience:
- Tamoxifen: Hot flashes, nausea, or an increased risk of blood clots.
- Aromatase Inhibitors: Joint pain, fatigue, and potential effects on bone density.
Here’s a comparison table of medication considerations to weigh before beginning treatment:
Table 3: Medication Considerations
| Medication | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen | Moderate to High | Hot flashes, nausea |
| Raloxifene | Moderate | Similar to Tamoxifen |
| Anastrozole | Varies | Joint pain, fatigue |
| Testosterone | Varies | Hormonal side effects |
Conclusion: The Necessity of Professional Guidance
Navigating the treatment landscape for gynecomastia requires tailored recommendations from a healthcare professional. Factors such as medical history, severity of the condition, and any underlying health issues should guide the selection of medication. Importantly, potential risks must be weighed against possible benefits, and ongoing monitoring is vital to ensure successful management of the condition. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any medication for enlarged male breasts, as personalized care is crucial to achieving the best results.
Surgical Options for Gynecomastia
When conservative measures such as lifestyle changes or medications fail to alleviate the discomfort associated with gynecomastia, surgical intervention becomes a viable option. Surgical procedures designed to correct enlarged male breasts are increasingly popular due to their success and the psychological benefits derived from achieving a more masculine chest contour. Below, we explore the various surgical options available for individuals seeking to address this condition.
Types of Surgical Procedures
There are several surgical techniques commonly employed to treat gynecomastia. The choice of surgery largely depends on the severity of the condition, the amount of excess breast tissue, and the patient’s overall goals. Here’s a breakdown of the main surgical approaches:
| Surgical Procedure | Description | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Liposuction | A minimally invasive procedure where excess fat is removed through small incisions. | Patients with primarily fatty tissue. |
| Glandular Excision | Surgical removal of the glandular breast tissue through an incision, typically around the nipple. | Patients with dense breast tissue. |
| Combined Procedure | A combination of liposuction and glandular excision for optimal results. | Patients with both fatty and glandular tissue. |
| Skin Reduction Surgery | In cases of significant excess skin, this approach also removes redundant skin. | Patients experiencing skin sagging. |
Understanding the Procedures
- Liposuction
- This technique is effective for individuals whose gynecomastia is mainly due to excess fatty deposits rather than glandular tissue. The surgeon uses a thin tube, or cannula, to suction out the fat while ensuring the surrounding tissues remain intact. As a result, this method offers minimal scarring and a quicker recovery time.
- Glandular Excision
- Suitable for cases where there is an enlargement of breast tissue itself rather than fat deposits, this surgery involves making an incision around the areola (the darker skin surrounding the nipple) to remove the glandular tissue. This method is particularly effective for more prominent gynecomastia and can provide a flatter, more contoured chest profile.
- Combined Procedure
- When both fatty and glandular tissues contribute to gynecomastia, surgeons often recommend a combined approach. By using both liposuction and glandular excision, patients can achieve comprehensive results, as this technique effectively targets multiple layers of tissue.
- Skin Reduction Surgery
- For those with significant sagging or excess skin following substantial weight loss or severe gynecomastia, skin reduction surgery can help. This procedure not only addresses breast volume but also tightens the chest area, enhancing cosmetic outcomes.
Factors to Consider
While surgical options can be highly effective, several factors should be contemplated before proceeding:
- Surgeon’s Expertise: The experience of the surgeon plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results. It is vital to consult a board-certified plastic surgeon with a strong background in gynecomastia surgeries.
- Recovery Time: Recovery times can vary based on the procedure performed; generally, patients might take about a week off from work. However, full recovery and the best results might take several months.
- Cost: Surgical options come with varied costs that might not always be covered by insurance. Discussing finances and potential payment plans with your surgeon’s office is advisable.
- Risks and Complications: Like any surgical procedure, there may be risks such as scarring, asymmetry, or infection. Informing your surgeon of any pre-existing conditions is important to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, surgical options for gynecomastia present effective solutions for those struggling with the emotional and physical challenges associated with enlarged male breasts. By exploring the various techniques available, individuals can make well-informed decisions tailored to their specific circumstances.
Recovery After Gynecomastia Surgery
Recovering from gynecomastia surgery is a crucial phase in the overall treatment process, as it directly influences the final aesthetic results and the patient’s emotional well-being. This section delves into the stages of recovery, what to expect post-surgery, and essential care tips that can facilitate a smooth healing journey.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
- Monitoring: Right after the gynecomastia procedure, patients are typically monitored in a recovery area to ensure stability in vital signs. Anesthesia effects can linger, so healthcare providers will assess comfort levels before discharge.
- Compression Garment: The patient is usually required to wear a compression garment for several weeks. This garment helps in minimizing swelling, supporting the chest area, and aiding in the skin’s retraction, leading to a more contoured appearance.
- Pain Management: Mild discomfort is normal following surgery, and physicians will generally prescribe analgesics to manage pain effectively. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen may also be used, but it’s essential to avoid NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen) in the initial days to minimize bleeding risks.
Typical Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline varies by individual circumstances, but generally follows this pattern:
| Time Frame | Activities and Limitations |
|---|---|
| First 24 to 48 Hours | Rest is paramount; avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting. Patients may feel groggy from anesthesia. |
| Week 1 | Swelling starts to decrease; light activities can be resumed. Follow-up appointments are typically scheduled. |
| Weeks 2-4 | Gradual return to normal activities; low-impact exercises such as walking can be resumed. Compression garments should still be worn as advised. |
| Month 1-3 | Most bruising and swelling should resolve. Gradually increase intensity in physical activities, but listen to your body. |
Key Considerations
- Wound Care: Keeping incisions clean and dry is vital to prevent infection. Patients should follow specific wound care instructions provided by their surgeon, which may include changing dressings or applying prescribed ointments.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can expedite recovery. Lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables are particularly beneficial as they provide necessary nutrients for healing.
- Emotional State: It’s common for emotional fluctuations to occur during recovery. Monitoring mental health, seeking support from friends or professionals, and allowing oneself to process the change can be essential components of recovery.
- Signs of Complications: Patients should be aware of potential complications, such as severe swelling, unexpected pain, or signs of infection (like fever or discharge). Immediate communication with a healthcare provider is crucial if any of these symptoms arise.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Routine check-ins with the surgeon are crucial for evaluating recovery progress and addressing any concerns. These appointments offer an opportunity for patients to discuss results and any lingering discomfort.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the recovery phase after gynecomastia surgery is marked by gradual progress and requires patience. Relying on professional guidance, asking questions, and adhering strictly to care instructions can significantly enhance recovery outcomes. It’s important to remember that full results may take several months to become visible, and taking care of both the body and mind during this time can yield positive results in the long run.
Preventing Gynecomastia in the Future
Preventing the occurrence of enlarged male breasts, often referred to as gynecomastia, requires a proactive approach that includes understanding risk factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and taking preventive measures. By implementing certain strategies, individuals may reduce the probability of developing this condition or mitigate its severity.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is fundamental in promoting overall health and preventing various conditions, including gynecomastia. Follow these dietary guidelines for optimal health:
| Food Category | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Aim for a variety of colors with at least 5 servings daily. |
| Whole Grains | Opt for brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread for fiber. |
| Lean Proteins | Include chicken, fish, legumes, and nuts for muscle health. |
| Healthy Fats | Choose avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish rich in Omega-3. |
Maintaining a healthy weight contributes significantly to hormonal balance, helping to avoid excessive fat accumulation that may influence breast tissue development.
Regular Exercise Regimen
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can help manage body weight and promote hormonal balance. Here are some effective types of exercise:
| Type of Exercise | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Training | Enhances overall fitness and aids weight control. For example, jogging or cycling for 150 minutes weekly is recommended. |
| Strength Training | Builds muscle mass, which in turn helps burn fat. Aim for at least two sessions a week targeting major muscle groups. |
| Flexibility and Balance | Activities like yoga can help alleviate stress, which may contribute to hormonal imbalances. |
Establishing a consistent workout routine aids in maintaining a healthy body composition and balancing hormones vital for normal male physiology.
Avoid Certain Substances
Certain substances are known to have direct effects on hormone levels, potentially increasing the likelihood of developing gynecomastia:
| Substance | Impact on Hormones |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | Excessive consumption may lead to liver damage, affecting hormone metabolism. |
| Anabolic Steroids | These substances can significantly disturb hormonal balance and promote breast tissue growth. |
| Recreational Drugs | Some drugs, including marijuana, have been associated with altered hormone levels. |
Reducing or eliminating these substances from one’s lifestyle can contribute to overall physical health and hormonal stability.
Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, particularly involving cortisol levels. Consider implementing stress-reduction techniques such as:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Allocate time to practice mindfulness or meditation. These techniques can significantly alleviate stress.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise not only improves physical health but also helps in reducing accumulated stress.
- Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Inefficient sleep patterns may elevate stress hormones and disrupt natural hormonal rhythm.
Routine Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital for catching any potential issues early on. Consult with a healthcare professional about:
- Hormonal Evaluations: Discuss any symptoms or concerns related to breast tissue or hormonal imbalances.
- Guidance on Medications: If on medication that may contribute to enlarged breast tissue, your doctor could suggest alternatives.
By following these preventive strategies—maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding disruptive substances, managing stress, and keeping up with medical check-ups—individuals can reduce the risk of developing gynecomastia and maintain healthier breast tissue. Remember, understanding the body’s signals and seeking early intervention can be vital in managing health proactively.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Recognizing the signs of enlarged male breasts can evoke a range of emotions, from embarrassment to concern. While gynecomastia is often not a serious health issue, certain situations warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional. Engaging a medical expert can ensure proper diagnosis and tailored treatment options, especially when the condition affects quality of life. Here, we outline key indicators and considerations for seeking professional advice regarding enlarged male breasts.
Key Indicators for Seeking Medical Consultation
There are specific circumstances that suggest the need for an appointment with a healthcare professional. These include:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent Enlargement | If breast tissue continues to grow or changes in size significantly over time, medical evaluation is recommended. |
| Discomfort or Pain | Any discomfort or pain in the breast tissue should prompt a consultation, as this may indicate an underlying issue. |
| Changes in Nipple Appearance | Changes such as swelling, discharge, or changes in nipple color could signal some medical concern. |
| Development of Lumps | The presence of lumps in the breast area should be thoroughly assessed to rule out potential pathologies. |
| Emotional Distress | If the condition significantly impacts self-esteem, mental health, or social interactions, professional help can be crucial. |
| Age Considerations | Pubertal development changes often resolve independently, but if symptoms persist into adulthood, evaluation is advised. |
Consultation Process
When considering a visit to a healthcare professional, individuals can expect to undergo a structured process involving the following steps:
- Initial Assessment
- During this stage, the healthcare professional will conduct a thorough medical history review, focusing on any changes in breast tissue and overall health.
- Physical Examination
- A detailed physical examination of the breast tissue will help the healthcare provider determine the extent of enlargement and identify any other anomalies.
- Diagnostic Tests
- Depending on the assessment, diagnostic tests such as blood tests, mammograms, or ultrasounds may be recommended to rule out other conditions.
- Review of Medications
- The provider will discuss any medications that could contribute to breast tissue changes, including anabolic steroids, certain antidepressants, and hormonal treatments.
Importance of Early Intervention
Timing can be critical when addressing enlarged male breasts. Early intervention allows for a broader range of treatment options and can prevent further emotional distress. Delaying a professional consultation may lead to more complex issues, requiring advanced treatments or surgical interventions to restore the individual’s sense of well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, seeking a consultation from a healthcare professional is crucial when dealing with symptoms related to enlarged male breasts. Whether the concern is physiological or emotional, timely intervention can help manage the condition effectively and support overall mental health. Remember that proactive steps in addressing health concerns are pivotal, paving the way for recovery and personal empowerment. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with a qualified healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes gynecomastia in males?
Gynecomastia in males can be attributed to various factors, including hormonal imbalances, obesity, certain medications, and underlying health conditions. Typically, it occurs when the levels of estrogen rise relative to testosterone in the body. This hormonal imbalance may result from puberty, aging, or conditions such as liver or kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, or tumors. Medications such as anabolic steroids, antidepressants, and some treatments for prostate cancer can also contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
What are the treatment options available for gynecomastia?
Treatment options for gynecomastia primarily depend on the severity and underlying cause. Non-surgical methods include lifestyle changes such as weight loss and exercise, which may reduce breast tissue in overweight individuals. Medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors can help adjust hormonal levels. In more severe cases, surgical intervention, known as gynecomastia surgery, may be recommended to remove excess breast tissue for a more contoured chest appearance.
Is gynecomastia surgery safe and what is the recovery process like?
Gynecomastia surgery, typically performed under general anesthesia, is considered safe with minimal risks when conducted by a qualified surgeon. Post-operative recovery generally involves wearing a compression garment to support the chest and reduce swelling. Patients usually return to normal activities within a few weeks, although strenuous exercise should be avoided for at least a month. It’s important to follow the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions for optimal healing and to discuss any concerns during follow-up appointments.
Can gynecomastia go away without treatment?
In many cases, gynecomastia, particularly when it occurs during puberty, can resolve on its own as hormone levels stabilize over time. For some adults, minor cases may not require treatment since they can remain stable and asymptomatic. However, if gynecomastia persists for more than a couple of years or becomes a source of discomfort or emotional distress, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential treatment options.
Does gynecomastia affect self-esteem?
Yes, gynecomastia can significantly affect an individual’s self-esteem and psychological well-being. Many men experience embarrassment, social anxiety, and reduced confidence due to the physical appearance of enlarged breasts. This perceived negative body image can lead to avoidance of social situations and impacts personal relationships. Professional help, such as therapy or support groups, may be beneficial for those struggling with self-esteem issues related to gynecomastia.