Reconstructive plastic surgery plays a vital role in restoring both form and function for individuals affected by trauma, illness, or congenital conditions. Throughout this blog post, we will explore the fascinating history of this medical field, delve into the various types of reconstructive procedures available, and discuss how innovations continue to shape its future. Moreover, we will highlight the significance of a multidisciplinary approach to patient care, emphasizing the importance of collaboration among healthcare professionals. Whether you’re considering a procedure for yourself or simply wish to learn more about how reconstructive techniques can enhance lives, join us on this enlightening journey through the world of reconstructive plastic surgery.
What is Reconstructive Plastic Surgery?
Reconstructive surgery serves a vital role in the medical field, aiming to restore both form and function to individuals who have experienced congenital anomalies, traumas, or surgical alterations due to disease. Unlike cosmetic procedures, which prioritize aesthetic enhancement, this type of surgery focuses on correcting physical defects or restoring areas of the body following injury or illness.
Key Objectives of Reconstructive Surgery
The primary goals of this surgery can be summarized as follows:
| Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Restoration of Function | The surgery aims to restore normal function to affected areas, improving mobility and daily living activities. |
| Correction of Deformities | It seeks to address physical deformities stemming from various causes, providing a more natural appearance. |
| Psychological Impact | By restoring appearance, it can alleviate psychological distress and improve the quality of life for patients. |
| Comprehensive Treatment | This approach often requires collaboration with various healthcare professionals to deliver holistic care. |
Common Indications for the Surgery
Reconstructive procedures may be indicated for a variety of circumstances, including:
- Trauma and Injury: Accidents can lead to significant injuries, including lacerations, fractures, or amputations. Surgical interventions focus on repairing structures, skin grafts, or even limb reconstruction.
- Congenital Anomalies: Conditions such as cleft lip and palate or congenital hand differences can significantly affect a person’s life. Surgical repair during infancy or childhood can facilitate normal development.
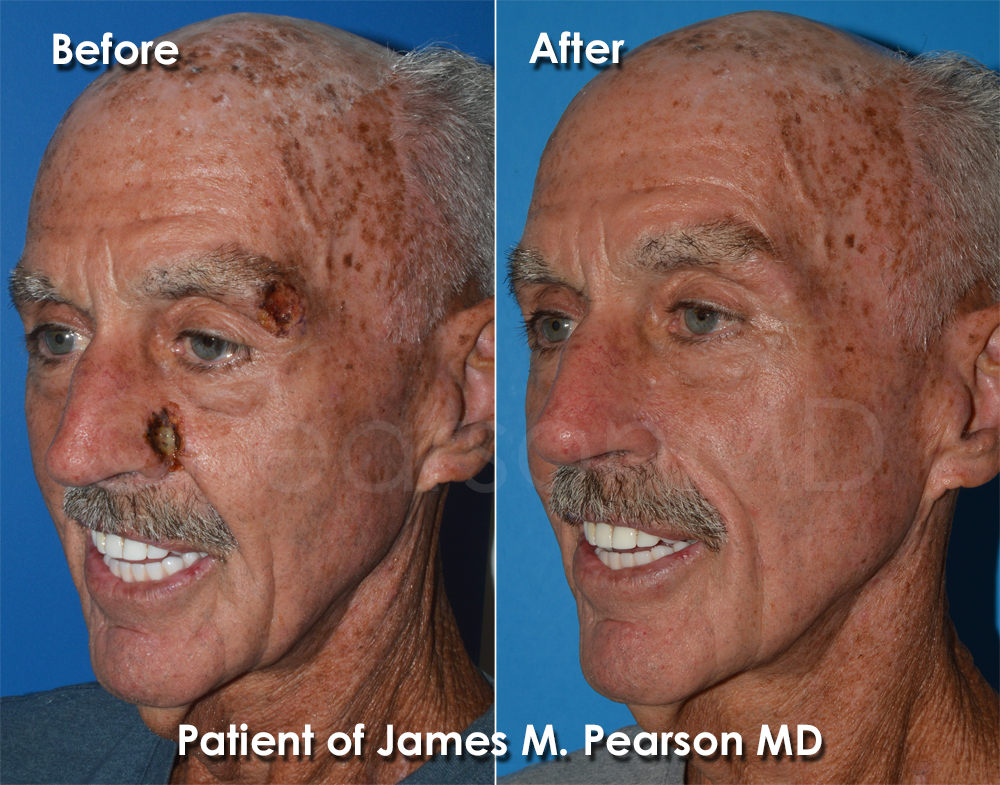
- Cancer Resection: Surgical removal of tumors often results in tissue loss. Repairing these defects is crucial for both functional and aesthetic reasons.
- Burns or Scarring: Severe burns can leave lasting scars. Techniques such as skin grafting or flap surgeries aim to restore function while improving the visual appearance of affected skin.
The Surgical Process
The process often involves a series of steps, which include pre-operative evaluations, the surgical procedure itself, and post-operative care.
- Preoperative Preparation: A thorough assessment including imaging studies, physical exams, and consultations with specialists helps craft a tailored surgical plan.
- Surgical Procedure: Depending on the complexity, various techniques may be employed, such as flap surgery (using adjacent tissue) or grafting (using skin from another part of the body).
- Postoperative Recovery: Adequate healing time, possibly requiring physical therapy, is crucial to ensure successful outcomes and regain functionality.
Importance of an Experienced Surgeon
Choosing a qualified physician specializing in this field is paramount. Surgeons skilled in this intricate discipline not only possess technical expertise but also a deep understanding of the emotional and psychological implications tied to physical appearance. A collaborative, patient-centered approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s wellbeing are addressed.
By bringing together medical expertise, empathetic care, and innovative techniques, this surgical branch presents opportunities for patients to reclaim both their physical identity and functional capabilities after life-altering events.
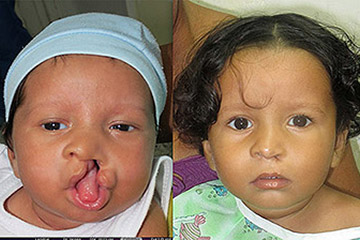
Reconstructive Surgery After Cancer: Restoring Identity
Reconstructive surgery plays a pivotal role in the lives of many individuals who have undergone cancer treatment. Reconstructive plastic surgery not only addresses physical alterations caused by the disease or its treatments but also significantly impacts emotional well-being and identity. This specialized surgery helps to restore not just the form of the body but also the psychological state of patients, allowing them to regain a sense of normalcy and confidence.
The Impact of Cancer Treatments
Cancer treatments, such as mastectomies, lumpectomies, and radiation therapy, often result in significant changes to a patient’s body. These changes can lead to feelings of loss, diminished self-esteem, and a struggle with body image. The psychological toll of these physical alterations can be overwhelming. Here are some of the common side effects of cancer treatments that may necessitate reconstructive surgery:
| Cancer Treatment | Physical Changes | Psychological Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mastectomy | Loss of breast tissue and shape | Emotional distress, body image issues |
| Lumpectomy | Altered breast shape and potential asymmetry | Feelings of incompleteness or unattractiveness |
| Radiation Therapy | Scarring and skin changes | Anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal |
| Head and Neck Treatments | Facial disfigurement and loss of function | Difficulty with identity, impact on communication |
Reconstructive Techniques Offered
Reconstructive surgery offers various techniques tailored to restore form and function based on the specific needs of the patient. Some common procedures include:
- Breast Reconstruction: Often performed after a mastectomy, this may involve implants or autologous (from the patient’s own body) tissue to recreate the breast.
- Facial Reconstruction: For those who have undergone head and neck surgeries, techniques like flap surgeries and bone grafts can help restore facial features and improve functionality.
- Tissue Expansion: This procedure gradually stretches the skin and tissue to prepare for reconstructive surgery in areas like the breasts or body.
- Skin Grafting: Used to replace missing or damaged skin, often a result of surgical excision or radiation damage.
The Psychological and Emotional Benefits
The benefits of reconstructive plastic surgery extend far beyond the physical realm. Successful surgical outcomes can lead to significant improvements in self-esteem, confidence, and overall quality of life. Many patients experience:
- Reclaiming Personal Identity: Patients report feeling ‘whole’ again after having reconstructive surgeries, which has a profound impact on their identity and how they view themselves in social situations.
- Improved Mental Health: Studies have shown that individuals who undergo reconstructive surgeries after cancer treatment often experience a decrease in anxiety and depression levels.
- Empowerment: Successfully overcoming cancer and rehabilitating their bodies helps patients feel empowered and more in control of their lives.
Important Considerations
While reconstructive surgery offers numerous benefits, it is essential for patients to consider a few factors before proceeding:
- Timing: Consult with healthcare providers about the best timeline for reconstruction after cancer treatment.
- Expectations: It is vital to have realistic expectations regarding outcomes, as reconstructive surgery may not restore the body to its original state.
- Support Network: Engaging with support groups and mental health professionals can enhance emotional resilience during the transitional journey.
In summary, reconstructive surgery after cancer serves as a beacon of hope, allowing survivors to restore their physical appearance and reclaim their identities. Each successful surgical intervention not only enhances the physical form but also empowers patients to move forward positively, signaling a beautiful new chapter in their lives.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Surgery
Navigating the recovery and rehabilitation process after reconstructive plastic surgery is crucial for patients aiming to restore both form and function. Understanding what to expect during recovery can significantly influence outcomes, minimize complications, and ensure the best possible healing.
Healing Phases
The recovery process can generally be divided into several key phases, each with distinct timelines and goals:
| Phase | Timeline | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Recovery | 1 to 7 days | Managing pain, preventing infection, initial healing |
| Early Recovery | 2 to 4 weeks | Reducing swelling, starting light mobility |
| Intermediate Recovery | 1 to 3 months | Regaining strength, increasing activity |
| Late Recovery | 3 to 12 months | Achieving full function, potential revisions |
Immediate Recovery Phase
During the first week post-surgery, patients often experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort. Managing these symptoms is critical. Doctors may prescribe pain medication and recommend ice therapy to reduce swelling. Additionally, staying hydrated and following post-operative care guidelines, including wound care, is essential to prevent infections.
Patients should plan for adequate rest. It is recommended to facilitate healing through limited physical activity. For this reason, arranging help at home for daily tasks can be beneficial during this phase.
Early Recovery Phase
After around one week, patients typically have follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers. This visit often involves removing stitches or drainage tubes, assessing healing progress, and tailoring rehabilitation plans. Under the guidance of a physical therapist, patients may begin light mobility exercises to restore range of motion without straining the surgical site.
Nutrition also plays a vital role during the early recovery phase. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins aids tissue healing and reduces the risk of complications.
Rehabilitation Techniques
The rehabilitation process after reconstructive plastic surgery often utilizes various techniques to facilitate recovery. These techniques may involve:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored physical therapy programs focus on restoring movement, strength, and functionality to affected areas. Therapists may use manual therapies, resistance training, and specialized movements.
- Occupational Therapy: For surgeries involving the hands or limbs, occupational therapists help patients regain the fine motor skills needed for daily activities. This may include exercises to enhance coordination and dexterity.
- Scar Management: Scar tissue can inhibit movement and cause discomfort. Specialized treatments like silicone sheets, massage therapy, or laser therapy can minimize scarring, improving both appearance and flexibility.
Psychological Considerations
Recovery from reconstructive surgery is not solely a physical journey. Patients may also experience emotional fluctuations as they navigate changes in appearance and functionality. Support from mental health professionals may help address feelings of anxiety and foster a positive self-image. Support groups or counseling can provide an essential outlet where patients share experiences and strategies for adaptation.
Final Stages of Recovery
Progress can be monitored progressively, and patients should communicate any concerns with their healthcare providers. Follow-up visits can help ascertain when patients can resume regular physical activities and hobbies. Full recovery can take time, but patience and adherence to rehabilitation protocols are key to achieving desired outcomes.
In summary, recovery and rehabilitation after reconstructive plastic surgery are multi-dimensional processes. Adequate planning, professional guidance, and emotional support collectively contribute to a successful transition to post-operative life, ensuring patients regain their functionality and confidence.
The Future of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery: Innovations and Advances
The field of reconstructive plastic surgery is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and innovative techniques that aim to enhance patient outcomes. As the demand for more effective and less invasive procedures rises, the future looks promising for both practitioners and patients alike. Below are several key innovations and advances anticipated to shape the future landscape of this specialized field.
1. 3D Printing Technologies
The incorporation of 3D printing technologies is revolutionizing how surgical procedures are planned and executed. This technology allows for the creation of customized implants and prosthetics tailored to the unique anatomy of each patient. Surgeons can now use precise anatomical models to plan surgeries more effectively, reducing the time spent in the operating room and improving surgical accuracy. Here’s a breakdown of how 3D printing is altering reconstructive procedures:
| Benefits | Details |
|---|---|
| Customization | Implants can be personalized, fitting individual patient needs. |
| Preoperative planning | Surgeons can practice complex procedures on 3D models. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Reduces the overall cost of procedures by minimizing complications. |
2. Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine is another frontier that continuously gains traction in reconstructive practices. This approach uses the body’s own cells to facilitate healing and regeneration of damaged tissues. Techniques like stem cell therapy and the use of growth factors help enhance the body’s natural ability to heal, making it a focal point for future developments. Notable aspects of this innovation include:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Utilizes cells that can differentiate into various tissue types, improving healing in soft tissue and bone.
- Tissue Engineering: Combines scaffolding and cellular materials to create structures that can support tissue regeneration.
3. Minimally Invasive Techniques
The trend towards minimally invasive surgical methods is paving the way for enhanced recovery experiences for patients. Techniques such as endoscopic surgery not only reduce scarring but also lead to shorter recovery times. This is how the emphasis on minimally invasive procedures is shaping future practices:
- Less Surgical Trauma: Reduced incision sizes lead to less damage to surrounding tissues.
- Faster Recovery: Patients experience less pain and quicker return to normal activities.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into surgical practices to aid in decision-making and predictive analytics. These technologies have the potential to:
- Analyze vast amounts of surgical data to improve outcomes and predict complications.
- Assist in diagnosis by analyzing imaging results more quickly and accurately than human counterparts.
5. Telemedicine Integration
With the rise of telemedicine, patient access and follow-up care are becoming more streamlined. Patients can now consult with their surgical teams remotely, allowing for preoperative assessments and postoperative follow-ups. This convenience enhances patient comfort and engagement, ensuring they remain informed throughout the process.
| Advantages of Telemedicine | Summary |
|---|---|
| Increased accessibility | Patients in remote areas can receive quality care. |
| Cost reduction | Minimizes travel expenses for consultations. |
| Enhanced patient monitoring | Facilitates timely adjustments to treatment plans. |
6. Bioengineered Tissues
The emergence of bioengineered tissues stands poised to change the game in reconstructive surgery. Scientists are developing solutions that use laboratory-grown tissues to replace or repair damaged areas, thus eliminating the complexities involved with grafts sourced from the patient or donors.
These advancements signal a future where reconstructive procedures can be performed with greater efficiency and success. As these innovations continue to emerge, the profession will undoubtedly witness drastic improvements in patient care, satisfaction, and overall outcomes. The alignment of technology with artistic surgical skill ensures that reconstructive approaches will not only restore form but will also significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals seeking these critical interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is reconstructive plastic surgery?
Reconstructive plastic surgery is a specialized area of surgery aimed at restoring form and function to parts of the body that may have been affected by trauma, congenital defects, disease, or previous surgeries. This field encompasses a wide range of procedures, including those for repairing facial structures after injury, reconstructing breasts post-mastectomy, and addressing severe burn injuries. The goal is to improve both the physical appearance and the functional capabilities of the surgical site, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life for the patient.
Who is an ideal candidate for reconstructive plastic surgery?
An ideal candidate for reconstructive plastic surgery is someone who has experienced physical deformities due to trauma, surgery, or congenital conditions that impact their appearance or function. Individuals who have realistic expectations about the outcomes of surgery and are in good overall health can be prime candidates. Additionally, candidates should understand the nature of the procedure, the recovery times involved, and any potential risks associated with the surgery. Consultation with a certified plastic surgeon is crucial to determining candidacy and receiving personalized recommendations.
What are the common procedures involved in reconstructive plastic surgery?
Common procedures in reconstructive plastic surgery include skin grafts, flap surgery, tumor removal, breast reconstruction post-mastectomy, cleft lip and palate repair, and hand surgery to restore function. Other specialized techniques may involve facial reconstructions following traumatic injuries or congenital issues. Each procedure is tailored to the patient’s specific needs and can help in restoring a more natural appearance as well as improving the functionality of the affected area.
What are the risks associated with reconstructive plastic surgery?
Like any surgical procedure, reconstructive plastic surgery carries certain risks, including infection, scarring, anesthesia complications, and dissatisfaction with the aesthetic results. There might also be potential risks specific to the site of surgery and the techniques employed. Pre-operative consultations typically address these risks comprehensively, allowing patients to make informed decisions, and to discuss any concerns with their surgeon, ensuring they are well-prepared for post-operative care and recovery.
How long does it take to recover from reconstructive plastic surgery?
Recovery duration from reconstructive plastic surgery depends on various factors, including the extent of the procedures performed, the individual’s overall health, and adherence to post-operative care instructions. Generally, patients may need to take several weeks off work, but most can expect to resume normal activities within a few months. Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing progress and address any complications that might arise. A personalized recovery plan will help facilitate a smooth healing process.