In recent years, discussions surrounding gender identity and affirmation have gained significant visibility, leading to an increased interest in the various surgical options available for those seeking to align their physical appearance with their true selves. Transgender operation is a complex and deeply personal journey, and understanding the variety of surgical procedures is essential for making informed decisions. This blog post aims to shed light on the critical aspects of gender affirmation surgery, ranging from facial feminization and chest procedures to genital reconstruction and body contouring. Additionally, we will explore the importance of informed consent, the role of non-surgical options, and the necessary post-operative care involved in this life-changing process. By the end of this guide, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the surgical paths available and the emotional support crucial for individuals throughout their transition.
Understanding Gender Affirmation Surgery
Gender affirmation surgery refers to a series of surgical procedures aimed at aligning an individual’s physical characteristics with their gender identity. For many, this surgical path is a critical component of transitioning, allowing individuals to express their true selves in a manner that reflects their internal experience. It serves as not just a medical intervention, but also a profound step toward mental well-being and overall quality of life.
Phases of Transition
Transitioning is a multifaceted process that encompasses several stages. Although each person’s journey is unique, the phases typically include:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Social Transition | Includes changes in gender expression, such as clothing, pronouns, and name. |
| Medical Transition | Involves hormone therapy, which may precede or accompany surgical procedures. |
| Surgical Transition | Encompasses various surgeries aimed at modifying physical attributes to match gender identity. |
The decision to pursue surgery is deeply personal and often coincides with significant reflection and emotional readiness. Many individuals experience feelings of dysphoria—the distress stemming from a discrepancy between their gender identity and their physical appearance. Gender affirmation surgery aims to alleviate this dysphoria.
Types of Procedures
There are several types of surgical options available, each designed to target specific aspects of an individual’s gender identity. These can broadly be categorized into:
- Facial Procedures: Such as facial feminization surgery, which alters features like the jawline, forehead, and nose to create a more traditionally feminine appearance. Conversely, specific surgeries can lend a more masculine contour to the face for those assigned female at birth.
- Chest Procedures: Chest masculinization (top surgery) alters breast tissue and may involve resizing or complete removal, while chest feminization may involve breast augmentation and contouring.
- Genital Reconstruction: These surgeries focus on changing the genitalia to match one’s gender identity and may include phalloplasty for transmasculine individuals and vaginoplasty for transfeminine individuals.
- Body Contouring: This includes liposuction, tummy tucks, or other methods to create or enhance body shape and definition according to the individual’s gender identity.
It’s worth noting that not all individuals choose to undergo every available surgical option, and outcomes may vary based on personal needs, health considerations, and desires.
Assessing Suitability for Surgery
Eligibility for these surgeries generally includes the following criteria:
- Informed Consent: Individuals should demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the procedures, risks, and post-operative care.
- Mental Health Support: A psychological evaluation may be required to ensure emotional readiness and to reiterate the importance of mental health throughout the journey.
- Hormone Therapy: Most surgeons mandate a certain period of living as one’s identified gender and may require hormone treatment prior to surgical intervention for optimal results.
Understanding these fundamentals allows individuals to engage in their journey with clarity and confidence, ultimately leading to a fulfilling transition. Informed decision-making is crucial, fostering a supportive environment where individuals can pursue surgery as a means of achieving authenticity and happiness in their lives.
The Importance of Informed Consent
Informed consent is a foundational aspect of any surgical procedure, but it carries heightened significance in the context of gender affirmation surgery. As individuals seek to align their physical bodies with their gender identities, understanding the implications, risks, and benefits of the various surgical options becomes crucial. This section delves into the importance of informed consent during the gender affirmation journey, emphasizing the patient’s autonomy, understanding, and empowerment.
Understanding Informed Consent
Informed consent is the process through which patients are educated about the characteristics of their proposed treatment, including its associated risks, benefits, and alternatives. This process serves to ensure that individuals make decisions regarding their health care that are informed, voluntary, and reflective of their values and preferences.
Key Components of Informed Consent
The informed consent process typically includes several essential elements:
| Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Disclosure | Patients must receive comprehensive information about the surgery, including its nature and objectives. |
| Understanding | Patients should demonstrate comprehension of this information, which often requires addressing questions and misconceptions. |
| Voluntariness | Consent must be given freely, without coercion or undue pressure from healthcare professionals or family members. |
| Capacity | Individuals must possess the mental and emotional capacity to make informed choices regarding their care. |
Empowerment Through Knowledge
Informed consent empowers individuals to take control of their transition journeys. By ensuring that patients are well-informed, healthcare providers foster an environment where individuals can voice their preferences and concerns. This leads to collaborations that prioritize patient well-being and satisfaction.
Moreover, knowledge about surgical options allows patients to set realistic expectations. Understanding potential outcomes, both physical and emotional, can alleviate anxiety and enhance the overall experience of gender affirmation.
Two-Way Communication
A crucial aspect of the informed consent process is the establishment of a two-way communication channel. Not only should healthcare providers guide patients through the complexities of their options, but they must also encourage open dialogue. This interaction should include discussions about the individual’s specific goals, personal circumstances, and any pre-existing medical conditions.
Encouraging questions and addressing uncertainty topics creates a trusting relationship between patients and healthcare providers. This collaboration often results in tailored surgical plans that resonate more closely with patients’ identities and desired outcomes.
The Role of Mental Health Professionals
Additionally, informed consent is often considered a collaborative effort that includes mental health professionals. They play a critical role in evaluating readiness for surgery, offering insights into the emotional and psychological aspects of the transition. Through mental health assessments and ongoing support, professionals can help decipher whether patients clearly understand the surgical implications, thereby reinforcing the informed consent process.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legally, informed consent serves to protect both the patient and the provider. Patients who are adequately informed and understand the risks involved are in a better position to make autonomous decisions, which can help mitigate misunderstandings and potential legal repercussions.
Ethically, the importance of informed consent aligns with the tenets of respect and dignity for all individuals. For many, the decision to undergo surgery is deeply personal, and it requires comprehensive guidance to ensure that all decisions align with their personal values and identities.
In summary, informed consent is not merely a formality; it serves as a fundamental building block in the journey of gender affirmation. It leads to empowerment, better communication, and a nuanced understanding of the surgeries, all pivotal components that enhance the transition experience.
Overview of Surgical Options: An Introduction
When it comes to gender affirmation, surgical options play a vital role in helping individuals align their physical appearance with their gender identity. These procedures can significantly enhance well-being and quality of life by alleviating gender dysphoria and promoting personal authenticity. To approach this journey thoughtfully, it is essential to understand the various surgical options available, the expected outcomes, and the potential risks involved.
Understanding Surgical Categories
Surgical options for gender affirmation can be categorized into different groups based on the area of the body they target. Below is a simplified table that highlights these categories and provides a brief overview of what each entails:
| Surgical Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Facial Surgeries | These procedures modify facial features to create a more masculine or feminine appearance. |
| Chest Surgery | Chest masculinization or feminization surgery alters the breast contour to align with gender identity. |
| Genital Surgery | This encompasses various surgeries that reconstruct genitalia to match one’s gender identity. |
| Body Contouring Procedures | These procedures modify body shape and fat distribution, enhancing physical characteristics. |
Detailed Insight into Each Surgical Option
Facial Surgeries:
Facial feminization and masculinization surgeries are designed to alter primary and secondary sexual characteristics visible on the face. These procedures can involve brow lifts, rhinoplasty (nose reshaping), jaw contouring, and cheek implants. The goals are to create a softer, more feminine appearance or a more angular, masculine one, depending on the individual’s identity.
Chest Surgery:
Surgical options for the chest differ dramatically based on an individual’s needs. Chest masculinization surgery often involves a double incision or a keyhole approach, removing breast tissue to create a flatter, more masculine chest. Conversely, chest feminization surgery may include breast augmentation using implants or fat transfer techniques to enhance breast shape and size.
Genital Surgery:
One of the most complex categories, genital surgeries involve a variety of techniques catering to both virilization and feminization. For example, vaginoplasty is performed to create a neovagina, while phalloplasty can be performed to construct a neophallus. Each of these procedures can involve multiple stages and different approaches tailored to the unique requirements and anatomy of the individual.
Body Contouring Procedures:
Body contouring focuses on enhancing overall body shape. This may involve liposuction to remove unwanted fat or various surgical interventions to enhance buttock and thigh appearance. Procedures such as gluteal augmentation can also assist individuals in achieving a more gender-conforming silhouette.
Factors Influencing Choice of Surgery
Several factors may influence the choice of surgical procedures. These include:
- Individual Goals: The specific desires for physical appearance and alignment with gender identity.
- Medical Considerations: Pre-existing health conditions that may affect surgical eligibility or recovery.
- Psychological Preparedness: Readiness for the physical and emotional changes that may occur post-surgery.
- Informed Consent: A thorough understanding of the risks, benefits, and realistic outcomes associated with each procedure.
Navigating the Surgical Journey
Choosing to undergo surgical options is a deeply personal and significant decision. It is essential for individuals to engage in thorough consultations with experienced healthcare professionals who specialize in gender-affirming procedures. These discussions should encompass the surgical process, recovery times, and potential complications, ensuring that individuals are well-prepared for their transformative journey.
In summary, the landscape of surgical options for gender affirmation is varied and comprehensive. Each individual’s journey will look different, aiming to align their physical bodies with their authentic selves. Taking the time to understand and explore these options is fundamental for anyone considering this path.
Facial Feminization Surgery
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a crucial aspect in the journey of many individuals seeking to align their physical appearance with their gender identity. This specialized surgical procedure encompasses various techniques intended to create a more feminine facial structure. For those who identify as transgender women or non-binary individuals, FFS can significantly enhance both confidence and quality of life. Below, we explore the key components, benefits, and considerations associated with facial feminization surgery.
Key Components of Facial Feminization Surgery
Facial feminization surgery includes an array of surgical techniques tailored to address specific facial features. The primary areas affected include:
| Facial Feature | Surgical Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Forehead | Forehead reduction and contouring | Smooths the forehead and reduces brow ridge |
| Nose | Rhinoplasty | Reshapes the nose to achieve a softer profile |
| Cheeks | Cheek augmentation | Enhances the fullness of the cheeks |
| Jawline | Jaw reduction | Creates a more tapered and refined jawline |
| Chin | Chin contouring | Softens the chin for a more delicate appearance |
| Adam’s Apple | Tracheal shave | Reduces the prominence of the Adam’s apple |
| Brow bone | Brow lift or contouring | Elevates the brow line and reduces protrusion |
These surgeries can be performed individually or in combination, depending on the person’s specific desires and anatomical considerations.
Benefits of Facial Feminization Surgery
- Improved Gender Dysphoria: Many individuals experience significant relief from gender dysphoria following FFS. By aligning their physical appearance with their gender identity, patients often report increased comfort in their own skin.
- Enhanced Self-Esteem: The transformation resulting from FFS can greatly enhance self-esteem. The psychological impact of feeling confident in one’s appearance is profound, leading to improved overall well-being.
- Social Acceptance: A more feminine facial appearance may aid in social interactions and acceptance in both personal and professional settings. This perceived alignment with societal gender norms can open doors for many.
Considerations Before Surgery
Before undergoing facial feminization surgery, it is essential to evaluate several factors, including:
- Informed Consent: It is vital that individuals thoroughly understand the risks and benefits associated with each procedure. Engaging in discussions with qualified medical professionals ensures informed decision-making.
- Costs and Insurance: FFS can be costly, and insurance coverage can vary greatly. Patients should discuss potential costs with their healthcare providers and check with their insurance for coverage options.
- Recovery Time: Depending on the complexity of procedures performed, recovery times can vary. Patients should be prepared for healing periods and follow-up care to achieve optimal results.
Potential Risks
As with any surgical procedure, FFS carries inherent risks, including:
- Infection
- Scarring
- Anesthesia complications
- Unsatisfactory aesthetic results
Individuals must weigh these potential risks against the anticipated benefits, making a well-informed decision about pursuing facial feminization surgery.
In summary, facial feminization surgery serves as a transformative option for individuals seeking to affirm their gender identity through physical changes. By understanding the various components, benefits, considerations, and risks, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving their desired outcomes. This surgery not only assists in reshaping appearances but also plays a significant role in fostering emotional and psychological well-being throughout the transition process.

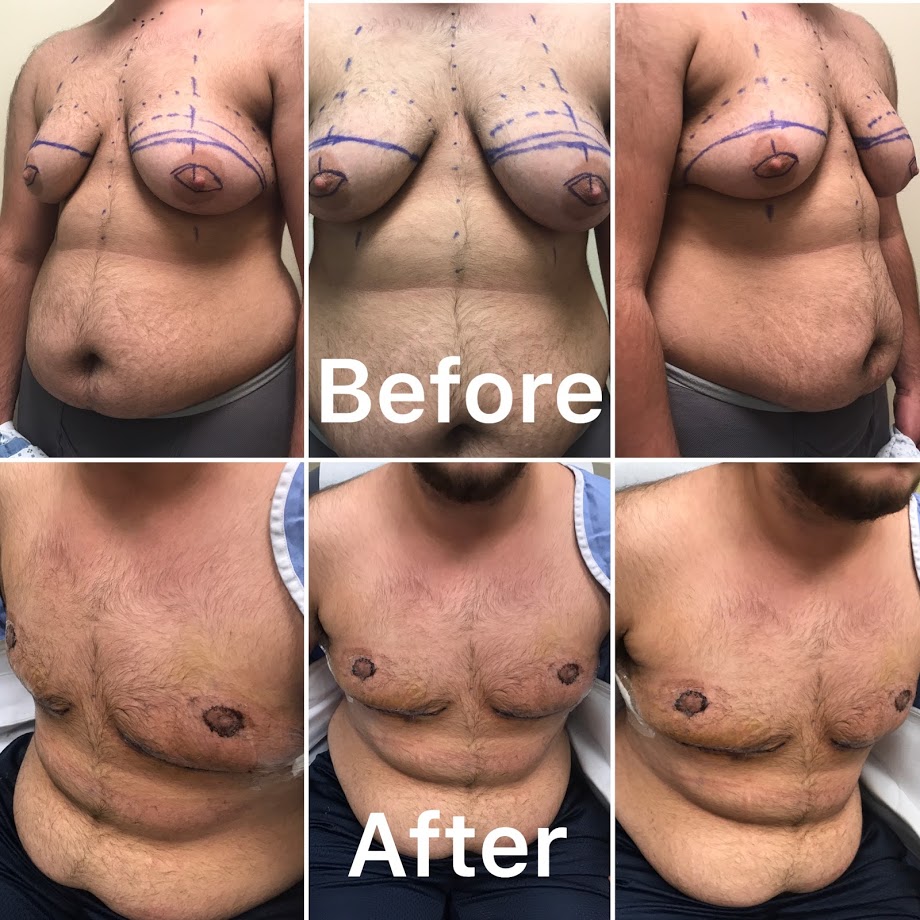
Chest Masculinization and Feminization
Chest surgery is a fundamental aspect of gender affirmation, enabling individuals to align their physical appearance with their gender identity. This process, often referred to as top surgery, encompasses procedures designed for different gender identities: chest masculinization for those transitioning to male and chest feminization for those transitioning to female. Each of these procedures addresses distinct anatomical and emotional needs, allowing individuals to experience a body that reflects their true selves.
Chest Masculinization Surgery
Chest masculinization surgery (also known as bilateral mastectomy with masculinization) aims to remove breast tissue and create a masculine-contoured chest. Understanding the surgical techniques and considerations can facilitate informed decision-making.
Surgical Techniques
| Technique | Description | Ideal Candidates |
|---|---|---|
| Double Incision | Two horizontal incisions under the breasts. | Those with larger breast tissue. |
| Periareolar | A circular incision around the nipple. | Suitable for individuals with smaller breast tissue. |
| Keyhole | A smaller incision beneath the nipple for minimal scarring. | Best for patients with minimal breast tissue. |
Chest Feminization Surgery
Chest feminization surgery (also known as breast augmentation or breast construction) aims to create a more feminine breast contour, enhancing overall body aesthetics. Options for this surgery often involve the placement of breast implants or the use of fat grafting.
Surgical Techniques
| Technique | Description | Ideal Candidates |
|---|---|---|
| Implant-Based | Placement of silicone or saline implants to enhance breast size and shape. | Individuals looking for more pronounced breasts. |
| Fat Grafting | Uses the patient’s own fat, harvested through liposuction, to create volume and shape. | Those desiring a more natural appearance with less invasive procedures. |
Considerations and Risks
Both types of chest surgery come with inherent risks and benefits. It is essential for prospective patients to have thorough discussions with medical professionals about their expectations, surgical options, and potential complications. Some common considerations include:
- Healing Time: Recovery varies; however, patients can typically expect a week to several weeks of downtime, depending on the procedure’s complexity.
- Scarring: Different techniques yield varying scar results. Awareness of potential scarring and aesthetic outcomes is crucial for both surgeries.
- Sensory Changes: Changes in nipple sensation can occur as a result of surgery, which is an important topic to address during consultations.
Patients must also consider emotional and psychological factors before undergoing chest surgery. The anticipation of aligning physical appearance with gender identity can be exhilarating yet daunting. Support systems, whether from friends, family, or healthcare professionals, play a vital role during this transition.
Support and Resources
Individuals considering chest masculinization and feminization surgery should access reliable resources to ensure they are equipped with comprehensive information. Engaging in support groups or forums, connecting with professionals knowledgeable in gender affirmation, and staying informed through credible medical websites can provide valuable insights.
The journey of gender affirmation through chest surgery is profoundly personal and transformative. Engaging in thoughtful discussions, understanding the surgical processes and risks, and seeking emotional support can aid in making informed decisions that resonate with one’s identity and aspirations.
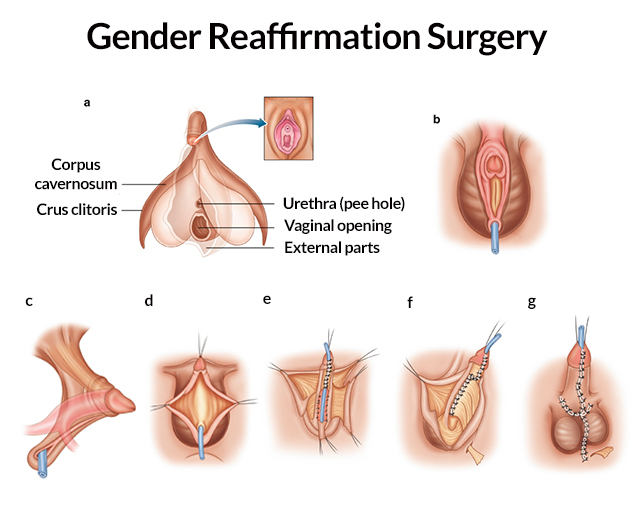
Genital Reconstruction Surgery
Genital reconstruction surgery plays a vital role in affirming an individual’s gender identity by aligning physical attributes with their self-identified gender. This form of surgery is designed primarily for transgender individuals and encompasses a range of surgical procedures suited to both male-to-female (MtF) and female-to-male (FtM) transitions.
Understanding the Procedures
Genital reconstruction may include various methods, each tailored to meet the specific needs and desires of the individual. Below is an overview of the common procedures involved in genital reconstruction for both MtF and FtM surgeries:
| Procedure | Target Group | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Penile Construction | FtM | Surgical creation of a penis using grafts from other body parts, often utilizing the forearm or thigh for skin and tissue. |
| Vaginoplasty | MtF | A procedure creating a vagina, typically using penile and scrotal tissue, or grafting skin from other areas. |
| Urethral Lengthening | FtM | Extending the urethra to allow for urination while standing, usually done during the penile construction process. |
| Orchiectomy | MtF | The removal of testicles to eliminate testosterone production, which can also form part of the MtF vaginoplasty. |
| Labiaplasty | MtF | Surgical alteration of the labia to create a more natural appearance. |
| Clitoroplasty | MtF | The creation or reconstruction of the clitoris during vaginoplasty, aimed at preserving sexual sensitivity and pleasure. |
Key Considerations
- Surgeon’s Experience: Selecting a surgeon with extensive experience in gender-affirming procedures is crucial. Researching their credentials, past work, and patient testimonials can help ensure a positive surgical experience.
- Health Assessments: A comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary before undergoing surgery. This assessment may include hormone therapy progress, mental health evaluations, and physical health checks to ensure that the patient is fit for surgery.
- Personal Goals: Understanding one’s motivations and goals for genital reconstruction is essential. This includes discussing aesthetic desires, functional expectations, and potential outcomes with the surgical team.
Post-Operative Expectations and Care
Post-operative care is critical in the recovery phase following genital reconstruction. Patients should be advised on the following aspects:
- Wound Care: Keeping the surgical area clean and following all recommended hygiene practices to prevent infection is vital for recovery.
- Pain Management: Regular communication with healthcare providers regarding pain levels allows for effective management using prescribed medications.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in light activities is encouraged once cleared by the surgeon, while avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities until fully healed.
Psychological and Emotional Factors
Transitioning involves more than just physical changes. Many individuals may face emotional challenges during the recovery period. Ongoing mental health support, such as therapy or support groups, can help individuals cope with the changes and emotions associated with their transition.
In sum, genital reconstruction surgery is an essential component of gender affirmation that significantly impacts many transgender people’s lives. The complexity of the procedures, combined with the importance of thorough pre-operative preparation and post-operative care, underscores the need for proper guidance and support throughout the journey. As awareness and understanding of these surgeries grow, individuals can approach their transitions with confidence in the options available to them.
Body Contouring Procedures
Body contouring procedures are essential components of gender affirmation surgery, designed to enhance physical appearance and align an individual’s body with their gender identity. These procedures focus on reshaping and enhancing specific areas of the body to create a more masculine or feminine silhouette, which can profoundly impact an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. Body contouring encompasses a variety of surgical techniques aimed at redistributing fat, removing excess tissue, and augmenting certain features. Below, we explore the diverse range of body contouring options available.
Key Body Contouring Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Targeted Areas | Aesthetic Goals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposuction | A surgical technique that removes excess fat deposits. | Abdomen, thighs, arms, and back | Contour and refine body shape |
| Fat Transfer | Involves harvesting fat from one area and injecting it into another. | Buttocks, breasts, and facial areas | Enhance volume and create a more feminine shape; can also be used for chest masculinization |
| Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty) | Removes excess skin and fat from the abdomen, tightening muscles. | Abdomen | A flatter, firmer abdominal contour |
| Thigh Lift | Reduces excess skin and fat in the thighs. | Inner or outer thighs | Smoother, more toned thigh appearance |
| Brachioplasty (Arm Lift) | Removes excess skin and fat from the upper arms. | Upper arms | More toned, firmer upper arms |
| Body Lift | Addresses sagging skin and fat in multiple areas of the torso. | Abdomen, thighs, and buttocks | Comprehensive contouring for overall body shape |
Benefits of Body Contouring
The benefits of body contouring procedures extend beyond mere aesthetic appeal. For many individuals undergoing gender affirmation, these surgeries are integral to achieving comfort in one’s own body and alleviating dysphoria. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced Appearance: Body contouring makes it possible to achieve a silhouette that aligns more closely with one’s gender identity, contributing to improved self-image and confidence.
- Improved Comfort: For individuals who experience discomfort due to excess skin or fat, these procedures can significantly enhance everyday comfort by allowing for greater mobility and ease in physical activities.
- Psychological Well-being: The positive transformation resulting from body contouring can lead to significant emotional and psychological benefits, as individuals may feel more accepted and confident in their identities.
Considerations for Body Contouring
Before undergoing body contouring procedures, individuals must take various factors into account:
- Health Evaluation: A thorough medical assessment ensures that the individual is suitable for surgery, assessing overall health, weight, and any underlying conditions that could complicate the procedure.
- Realistic Expectations: It is crucial for patients to have realistic expectations about the outcomes. While body contouring can offer substantial enhancements, results may vary based on individual circumstances and factors.
- Recovery Time: Recovery from body contouring procedures varies, typically ranging from a few weeks to months, depending on the extent of the surgery. Patients need to follow post-operative instructions carefully to ensure proper healing.
Choosing to undergo body contouring procedures is a deeply personal decision and can significantly influence one’s gender affirmation journey. Consulting with qualified and experienced surgeons is essential to explore options, understand risks, and achieve the desired results tailored to individual needs. With the right information and support, body contouring can be a transformative step in the pursuit of aligning one’s physical appearance with their true identity.
Post-Operative Care and Considerations
Undertaking gender affirmation surgeries involves a significant commitment to self-care and recovery post-operation. The post-operative phase is crucial for ensuring optimal outcomes, supporting healing, and adapting to one’s new body. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the essential aspects of post-operative care and considerations that individuals should keep in mind throughout their recovery journey.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Immediately following surgery, patients enter a recovery phase in which close monitoring is crucial. Care typically begins in the hospital under the supervision of healthcare professionals. Here are some key components of immediate post-operative care:
| Care Component | Importance |
|---|---|
| Monitoring Vital Signs | Ensures the patient is stable and recovering without complications. |
| Pain Management | Alleviates discomfort using prescribed medications, crucial for healing. |
| Fluid Intake | Maintains hydration and aids in the recovery process; intravenous fluids may be necessary initially. |
| Surgical Site Care | Regular checks for infection, bleeding, or unusual inflammation are mandatory to ensure proper recovery. |
Home Care Guidelines
Once discharged, patients must adopt a diligent home care regimen that focuses on both physical healing and emotional well-being. Consider the following guidelines:
- Medication Adherence: Consistently taking prescribed medications will facilitate pain management and curb the risk of infections.
- Rest and Recuperation: Engaging in adequate rest is vital, as it allows the body to heal. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for the designated recovery period, which may vary by surgical type.
- Wound Care: Keep the surgical site clean and dry. Follow specific instructions regarding dressing changes, bathing, and signs of infection to monitor.
- Nutritional Support: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps in tissue repair. Adequate protein intake is particularly important for wound healing.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up visits with the surgeon to monitor recovery progress and address any concerns. Advanced imaging or tests may be required to ensure everything is healing correctly.
Managing Emotional and Mental Health
Transitioning can take a toll on mental well-being. It’s important to proactively manage emotional health alongside physical recovery. Here are notable tips:
- Therapy and Counseling: Regular sessions with a mental health professional experienced in gender identity issues can be extremely beneficial. They can provide adjustments to cope with changes and recovery challenges.
- Support Groups: Consider joining support groups that foster connection with others who are undergoing similar experiences. Sharing feelings and stories can promote healing and foster a sense of community.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can ease anxiety and enhance emotional stability.
Monitoring for Complications
Vigilance for any post-operative complications should be part of the recovery plan. Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they experience:
| Warning Sign | Possible Concern |
|---|---|
| Increased bleeding | Could indicate a hematoma or adverse surgical reaction. |
| Severe swelling | May point to infection or fluid accumulation. |
| Persistent pain not alleviated by medication | Might indicate complications requiring medical attention. |
| Fever over 101°F (38.3°C) | Could signal an infection or other serious issues. |
By adhering to these post-operative care practices, individuals can optimize their healing process and foster a smooth transition into the next chapter of their lives. Remember, this journey encompasses both physical and emotional dimensions, and seeking help when needed will only serve to enrich the overall experience.
Emotional and Psychological Support During Transition
Transitioning is a deeply personal and multifaceted journey that involves not just physical changes, but also considerable emotional and psychological shifts. It is essential to understand that the emotional experience of transitioning can be both transformative and challenging. Therefore, having robust emotional and psychological support during this process is crucial for overall well-being.
The Importance of Emotional Support
Many individuals undergoing transition experience a range of emotions, including joy, anxiety, fear, and uncertainty. Support systems play a vital role in navigating these feelings. Here are some key elements to consider regarding emotional support:
| Key Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Family and Friends | Having a supportive network of family and friends can significantly impact one’s transition experience. Open conversations about feelings and changes can foster understanding and closeness, allowing allies to support effectively. |
| Support Groups | Joining support groups, either in-person or online, provides individuals with a sense of community. Sharing experiences and hearing others’ stories often reduces feelings of isolation and promotes mental resilience. |
| Therapeutic Support | Engaging with a mental health professional who specializes in gender identity issues is crucial. Therapy can provide a safe space to explore feelings, cope with anxiety, and develop strategies to navigate challenges effectively. |
| Peer Counseling | Connecting with peers who have experienced similar journeys can be immensely beneficial. Peer counseling can foster understanding, provide relatable insights, and help in developing coping mechanisms. |
Managing Emotional Challenges
Transitioning often brings emotional challenges that can influence mental health. Here are some common issues faced and strategies to manage them:
- Anxiety and Depression: Many experience heightened anxiety or depression during transition. Regular scheduling of therapy can assist in managing these feelings effectively.
- Identity Confusion: Questions about identity can lead to confusion and distress. Engaging in self-reflection activities, such as journaling or art therapy, can help individuals clarify their feelings.
- Fear of Acceptance: Worries about acceptance from society, family, and friends can be daunting. Group therapy sessions focusing on self-acceptance strategies can foster resilience and a positive self-image.
- Social Isolation: The fear of isolation may prevent individuals from expressing themselves fully. Joining LGBTQ+ organizations or local meetups can create supportive networks and alleviate feelings of loneliness.
Resources for Effective Support
Accessing the right resources is crucial for emotional and psychological support during transition. Here are valuable avenues to explore:
| Resource Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Counseling Services | Many organizations offer counseling explicitly for transgender individuals. Therapy can focus on identity exploration, coping strategies, and building emotional resilience. |
| Hotlines | Confidential hotlines provide immediate support for anyone in crisis. These services can offer advice, referrals, or simply a listening ear. |
| Online Forums and Communities | Various online platforms allow for connection with others in similar situations. These forums facilitate discussions that empower individuals and share vital resources. |
| Books and Literature | Reading material on gender identity and transition can provide insights and strategies for emotional management. Books authored by individuals who have transitioned often resonate deeply. |
Emotional and psychological support during transition is critical to ensuring a pathway toward a fulfilled and authentic life. By nurturing well-being through various support systems and resources, individuals can embark on their journeys more confidently and joyfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gender affirmation surgery?
Gender affirmation surgery, often known as gender-affirming surgery or sex reassignment surgery, is a medical procedure that helps individuals transition from one gender to their recognized gender. This type of surgery can include a variety of procedures tailored to meet the individual’s needs, such as chest masculinization or breast augmentation for transgender men and women, respectively, as well as genital surgeries like vaginoplasty or phalloplasty. The ultimate goal is to align an individual’s physical body with their gender identity, thereby alleviating gender dysphoria and improving mental health and well-being.
What are the different types of surgical options available?
There are several surgical options for gender affirmation, which can be broadly categorized into two groups: top surgery and bottom surgery. Top surgery typically refers to procedures that alter the chest, such as chest masculinization for transgender men or breast augmentation for transgender women. Bottom surgery encompasses various genital surgeries, including vaginoplasty, which constructs a vagina, and phalloplasty, which constructs a penis. Other procedures may include hysterectomy, orchiectomy, and facial feminization surgeries. The choice of procedure largely depends on individual preferences, goals, and medical considerations.
What is the recovery process like after gender affirmation surgery?
The recovery process following gender affirmation surgery can vary significantly based on the type of procedure performed and individual factors. Generally, patients can expect a recovery period that ranges from a few weeks to several months, with varying levels of discomfort, swelling, and bruising. It is crucial for patients to follow their surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, which often include managing pain, taking prescribed medications, and adhering to follow-up appointments. Psychological support is also essential during recovery, as individuals may experience a range of emotions as they adjust to their new bodies.
Are there any risks associated with gender affirmation surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, gender affirmation surgeries come with certain risks and potential complications. Common risks include bleeding, infection, scarring, and anesthesia-related issues. In rare cases, more severe complications may occur, such as nerve damage or dissatisfaction with aesthetic results. Therefore, it is essential for patients to choose a qualified, experienced surgeon and to have thorough discussions regarding the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of the procedures they are considering. Additionally, pre-surgical counseling can help manage expectations and prepare individuals for the changes ahead.
How can individuals prepare for gender affirmation surgery?
Preparation for gender affirmation surgery involves both physical and emotional aspects. It often begins with consultations with healthcare providers specializing in transgender health, who will provide guidance on suitable surgical options and what to expect. Physical preparation may include lifestyle adjustments such as nutrition and exercise to optimize health ahead of the operation. Emotionally, individuals might benefit from counseling to explore their feelings and expectations related to the transition. Additionally, securing post-operative care and support systems, including family, friends, or support groups, can greatly enhance recovery.