Breast reconstruction can be a significant step for individuals recovering from breast cancer, and understanding the various options available is essential for making informed decisions. One innovative method gaining attention is the DIEP flap procedure, which utilizes tissue from the abdomen to create a natural-looking breast mound. In this blog post, we will delve into what the DIEP flap procedure entails, explore its numerous benefits, and discuss who makes a suitable candidate for surgery. Additionally, we’ll walk you through the entire surgery process, recovery expectations, and potential risks, while comparing it to other reconstruction methods. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with valuable insights and answers to frequently asked questions about this transformative procedure. Join us as we navigate through the world of breast reconstruction with the DIEP flap technique.
What is the DIEP Flap Procedure?
Breast reconstruction has evolved significantly over the years, providing women with an opportunity to restore their breast shape and appearance after mastectomy or lumpectomy. One of the leading techniques in this area is the DIEP flap procedure, which not only emphasizes aesthetic results but also prioritizes the patient’s overall well-being by utilizing their own tissue.
Understanding the Fundamentals
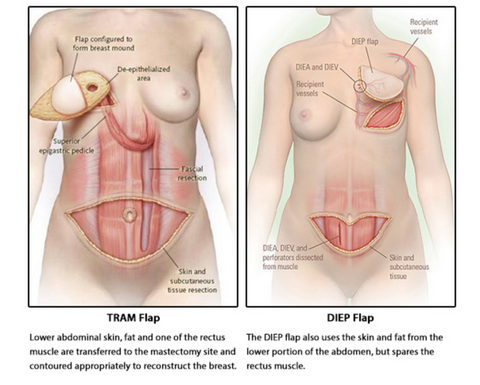
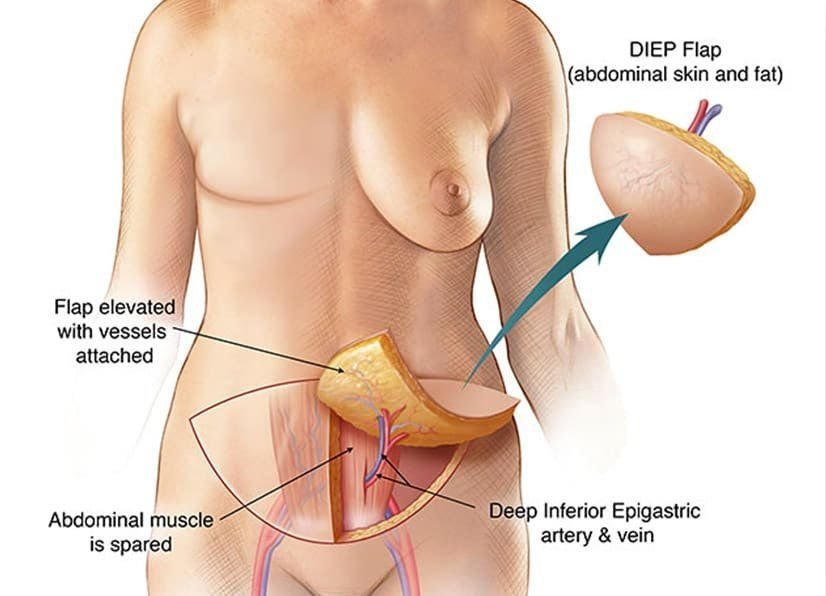
The acronym “DIEP” stands for Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator. This surgical method involves harvesting skin and fat from the lower abdomen to create a new breast. Unlike other flap procedures that may involve muscle transfer, this technique preserves the abdominal muscles by only taking blood vessels and tissue, minimizing postoperative complications and recovery time.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components involved in this procedure:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Tissue Source | Skin and fat are obtained from the lower abdominal area (the “donor site”). |
| Blood Supply | The procedure utilizes the deep inferior epigastric artery and its branches to ensure a reliable blood supply. |
| Muscle Preservation | Muscles remain intact, which aids in the rehabilitation process and reduces pain. |
| Aesthetic Result | The soft tissue mimics the natural contour of a breast, leading to realistic reconstructions. |
The Surgical Procedure
The surgical process typically lasts between 6 to 8 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. The steps involved include:
- Harvesting Tissue: The surgeon makes an incision in the abdominal area to remove a flap of skin and fat while carefully preserving the associated blood vessels.
- Reconstructing the Breast: The harvested tissue is then expertly shaped and attached to the chest wall where the breast was removed.
- Connecting Blood Vessels: Surgeons carefully connect the blood vessels from the flap to the blood vessels in the chest area, ensuring proper circulation.
- Closing the Incisions: Both the donor site and the breast reconstruction area are closed with sutures to promote healing.
Advancements in Techniques
Moreover, the DIEP flap procedure has been enhanced through the use of microsurgical techniques which allow for intricate reconnection of blood vessels. This advancement leads to faster recovery times, reduced complications, and improved overall outcomes for surgical patients.
Who Can Benefit?
This procedure is particularly beneficial for women seeking a natural reconstruction result without the possible complications associated with implants. Moreover, it can also provide abdominal contouring, giving dual benefits to the patient’s overall aesthetic appearance. However, it is essential to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to evaluate individual suitability and to discuss any concerns.
In summary, the DIEP flap procedure represents a sophisticated option for breast reconstruction that harmonizes functionality with aesthetics, advocating for patient comfort and well-being throughout the surgical journey. By utilizing the body’s own tissue, it not only supports healing but also achieves natural-looking results that many women desire after breast cancer surgeries.
Benefits of the DIEP Flap for Breast Reconstruction
The DIEP flap procedure (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator flap) stands out as a preferred method for breast reconstruction after mastectomy or significant breast tissue loss. This technique utilizes the patient’s own abdominal tissue, ensuring not only an aesthetic outcome but also functional benefits. Below, we explore the numerous advantages that the DIEP flap procedure can offer.
Aesthetic Advantages
One of the primary benefits of the DIEP flap is its ability to create a natural-looking breast shape. Surgeons harvest skin and fat tissue from the lower abdomen, which closely resembles the soft texture and contour of breast tissue. This technique enables a more balanced and symmetrical appearance in comparison to synthetic implants. Additionally, the natural tissue used in the DIEP flap reduces the risk of complications commonly associated with implants, such as rupture or capsular contracture.
No Muscle Sacrifice
Unlike other flap procedures, such as the TRAM flap, the DIEP flap preserves the abdominal muscles because only the skin and fatty tissue are used. This key distinction minimizes postoperative pain and complications related to muscle weakness, providing patients a quicker return to their normal activities. The preservation of these muscles also supports better functionality in the abdominal region, allowing for improved core strength and stability post-surgery.
Reduced Recovery Time
Patients undergoing the DIEP flap procedure typically experience a shorter recovery period compared to those who opt for traditional implant reconstruction. Although the initial healing process may take some time, the risk of complications is significantly lower, which translates to fewer follow-up procedures. Many patients report a return to baseline activities within weeks rather than months, making the DIEP flap a favorable option for those who prioritize a swift recovery.
Long-Lasting Results
The results of the DIEP flap can be remarkably durable. Since the reconstructed breast is made from the patient’s own tissue, it ages naturally alongside the rest of the body. This means that as weight fluctuates or changes occur due to aging, the reconstructed breast will adjust accordingly, providing a more consistent appearance over time.
Improved Body Contour
Another noteworthy advantage of the DIEP flap procedure is the secondary benefit of abdominal contouring. The removal of excess skin and fat from the abdomen not only aids in breast reconstruction but also enhances the overall body shape. This dual effect is often appreciated by patients, as they enjoy a flatter stomach in addition to a more aesthetically pleasing breast.
Table of Key Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural Aesthetic | Creates a breast that closely resembles the look and feel of healthy breast tissue, ensuring a natural appearance. |
| Preservation of Muscle | Utilizes only skin and fat, maintaining abdominal muscles for improved strength and functionality. |
| Quicker Recovery | Generally allows for a faster return to daily activities compared to traditional implants, with lower risk of complications. |
| Longevity of Results | Offers a lasting outcome that ages naturally, adapting to changes in the body over time. |
| Body Contouring | Reduces excess abdominal tissue, enhancing the overall body shape while achieving breast reconstruction. |
By opting for the DIEP flap procedure, patients not only receive a beautifully crafted breast but also gain additional health and aesthetic benefits. This intricate surgery is more than just a reconstructive technique; it embodies a holistic approach to restoring confidence and enhancing well-being.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for DIEP Flap Surgery?
Determining suitability for the DIEP flap procedure involves a comprehensive evaluation, taking into account both medical and personal factors. This innovative surgical option is designed to restore breast shape following mastectomy or severe breast deformities. However, not every patient may be ideal for this type of breast reconstruction.
Essential Considerations for Candidacy
Several key criteria can help assess whether a patient is a suitable candidate for the DIEP flap procedure:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Type of Breast Cancer | Patients undergoing mastectomy or lumpectomy for breast cancer commonly qualify. |
| Health Status | Good overall health, particularly in terms of cardiovascular health, is essential. |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | An ideal BMI (typically below 30) is crucial, as higher BMI can affect surgical outcomes. |
| Tissue Availability | Adequate abdominal tissue (fat and skin) must be available for the flap procedure. |
| Non-Smoker | Smoking can impede blood flow and healing; candidates should ideally be non-smokers. |
| Emotional Readiness | Emotional stability and readiness for potential changes in body image are vital. |
| Realistic Expectations | Patients must have realistic expectations about the results of the surgery. |
Medical Conditions That May Affect Candidacy
Certain medical conditions could disqualify a patient from being a good candidate for the DIEP flap procedure. Understanding these conditions is crucial for both patients and their healthcare providers. Here’s a look at common medical conditions that pose challenges:
| Medical Condition | Impact on Suitability |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Poorly controlled diabetes can slow healing and increase infection risk. |
| Obesity | Excess weight can complicate surgery and recovery, impacting overall outcomes. |
| Cardiovascular Issues | Heart problems or hypertension may present risks during surgery. |
| Chronic Lung Disease | Respiratory issues could complicate anesthesia and recovery. |
| Autoimmune Disorders | These may affect healing processes and increase risks of complications. |
Psychological Considerations
Patients considering the DIEP flap procedure should also be evaluated on psychological grounds. The emotional aftermath of breast reconstruction is significant and can vary widely among individuals. Factors that can impact psychological suitability include:
- Support Systems: Strong family and social support can enhance a patient’s readiness for surgery.
- Mental Health: Pre-existing mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety, should be managed with the help of a professional prior to surgery.
- Understanding of the Procedure: Patients should possess a clear understanding of the potential outcomes and risks associated with the DIEP flap procedure.
Age and Breast Reconstruction Choices
Age is another critical factor in evaluating candidacy. Younger patients may have more remaining breast tissue or skin elasticity, which may favor surgical outcomes. Conversely, older patients may have health-related concerns that could complicate surgery. Ultimately, age must be considered alongside individual health factors and personal motivations for surgery.
By conducting a thorough assessment that examines medical, physical, and psychological aspects, healthcare providers can determine the most suitable candidates for the DIEP flap procedure. This careful consideration not only maximizes the success of the surgery but also supports a smoother recovery process, ensuring patients receive the breast reconstruction outcomes they hope for.
The Surgery Process: Step-by-Step Overview
Embarking on the journey of breast reconstruction through the DIEP flap procedure involves several well-defined steps. Understanding what to expect during each phase can alleviate apprehensions and help patients prepare for the surgery. Below is a detailed breakdown of the surgical process, which integrates meticulous planning and precise execution.
Pre-Surgery Evaluation
Before the actual surgery, a thorough pre-operative assessment takes place. This stage may include:
- Medical History Review: The surgeon evaluates the patient’s history of breast cancer, previous surgeries, and overall health status.
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive examination is performed to ascertain the viability of donor tissue from the abdomen.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques like MRI or ultrasound might be employed to assess the tissue’s suitability.
- Discussion of Goals: Patients can discuss their aesthetic goals and any concerns with the surgical team, fostering clear communication.
Anesthesia Administration
On the day of the surgery, patients are first given an anesthetic. Generally, general anesthesia is used during the DIEP flap procedure, ensuring that patients remain pain-free and unconscious throughout the surgery.
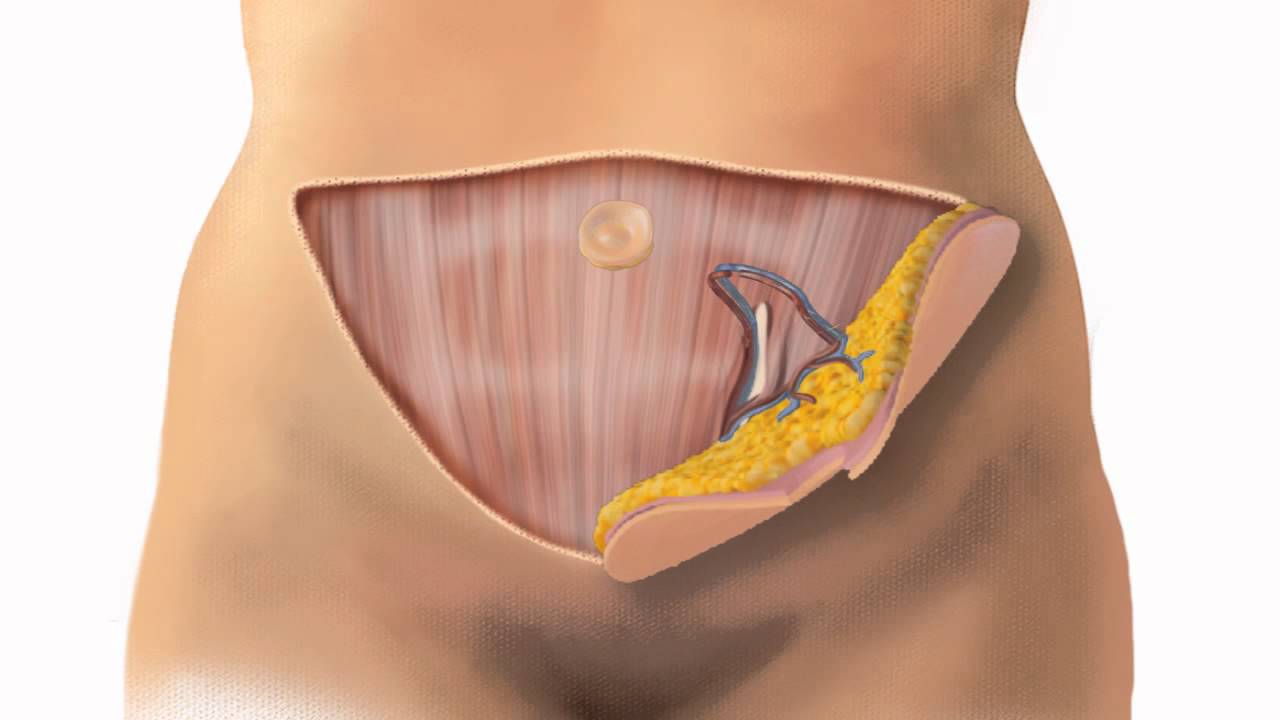
Step 1: Flap Harvesting
The DIEP flap procedure derives its name from the deep inferior epigastric perforators, which are blood vessels supplying the abdominal skin and fat. In this initial step, the surgeon conducts the following:
- Incision Creation: A horizontal incision is made along the lower abdomen, similar to a “tummy tuck” incision.
- Tissue Dissection: The surgeon carefully dissects the skin and fat, preserving the blood vessels and nerves that will be essential for transplanting the flap to the breast area.
Step 2: Flap Transfer
Once the flap is harvested, the next phase involves moving it to the breast site:
- Preparing the Breast Area: A separate incision is made in the breast region, allowing the surgeon to create a space for the flap.
- Microvascular Anastomosis: Here, the surgeon meticulously connects the blood vessels of the harvested tissue to the recipient blood vessels in the chest. This step is critical, as proper circulation is necessary for the survival of the transplanted flap.
Step 3: Completing the Reconstruction
With the flap in place, the surgeon proceeds to finalize the reconstruction:
- Shaping the Breast: The flap is sculpted into a breast mound that simulates a natural breast’s appearance.
- Incision Closure: The surgeon then sutures the incisions in both the abdomen and the breast area, ensuring that they are closed securely to minimize scarring.
Post-Operative Monitoring
After the surgery, patients are closely monitored in a recovery room. The medical staff checks vital signs and ensures that the flap is receiving adequate blood flow. This initial observation lasts a few hours before patients are moved to their hospital room for further recovery.
Summary Table of the Surgical Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-Surgery Evaluation | Comprehensive review of medical history, physical checks, and imaging studies. |
| Anesthesia | General anesthesia is administered for patient comfort and pain relief. |
| Step 1: Flap Harvesting | Incision on the abdomen, dissection of skin and fat, and preservation of blood vessels. |
| Step 2: Flap Transfer | Creating a breast incision, transferring the flap, and connecting blood vessels. |
| Step 3: Completing Reconstruction | Shaping the breast mound and closing incisions securely. |
| Post-Operative Monitoring | Vital signs are checked, and the flap’s blood flow is assessed. |
Understanding the surgery process can significantly contribute to a patient’s confidence and preparedness for their DIEP flap procedure. By having clarity on each step, from the initial evaluation to post-operative care, patients can approach their reconstructive journey with enhanced peace of mind.
Recovery and Healing After a DIEP Flap Procedure
The recovery journey following reconstructive surgery can often feel like a multi-phase expedition, especially after a diep flap procedure. Understanding the healing process and the expected timeline is crucial for patients. This procedure involves the transfer of tissue from the abdomen to the breast area, making the recovery slightly different from other methods. Below, we outline what patients can anticipate during their recovery.
Immediate Post-Operative Period
Upon awakening from anesthesia, patients might experience grogginess and confusion. Recovery begins in the hospital, generally lasting for 2 to 5 days. Key aspects of this initial phase include:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Monitoring | Vital signs and surgical site closely checked |
| Pain Management | Effective pain control through medications |
| Mobility | Gradual increase in movement encouraged |
During the first few days, it’s common for patients to feel some discomfort at both the donor site (abdomen) and the reconstructed breast. Nurses will assist in managing pain through prescribed analgesics and will monitor for any signs of complications, such as excessive bleeding or infection.
At Home: Early Recovery Phase
Once discharged from the hospital, the recovery process continues at home. Generally, patients are advised to take it easy for at least two to four weeks. Essential elements during this phase include:
- Rest and Relaxation: Prioritizing rest helps the body repair itself. Daily activities should be limited, avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous exercise.
- Care for Wounds: Keeping the surgical sites clean and dry is crucial. Patients will receive specific instructions on caring for their incisions, which may involve changing dressings and watching for signs of infection.
- Follow-up Appointments: Scheduled visits with surgeons are necessary to monitor healing and remove stitches, if applicable.
Mid to Late Recovery Phase
As recovery progresses, typically around 4 to 8 weeks post-surgery, patients may gradually return to more normal activities. At this stage, several improvements can be expected:
| Recovery Milestone | Duration |
|---|---|
| Decreased Discomfort | Pain and swelling significantly reduce |
| Increased Mobility | Patients can engage in light physical activities |
| Enhanced Aesthetics | Final results start to become visible |
It’s essential for patients to continue to listen to their bodies and not rush the healing process. Activities like walking are encouraged, as they enhance circulation without straining the surgical sites.
Long-Term Recovery Considerations
The complete healing process can take up to a year. Follow-up care during this time is vital to ensure optimal recovery. Several factors contribute to long-term outcomes, such as:
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a healthy diet and normal exercise routine can facilitate recovery.
- Emotional Well-being: Psychological support is critical, as emotional healing often takes as much time as physical recovery.
- Continued Communication: Regular updates to the healthcare team about any concerns during recovery are advised.
Patient Support and Resources
Support systems play a vital role in recovery. Engaging family members and friends can alleviate both physical and emotional burdens. Furthermore, participating in support groups with others who have undergone similar surgeries can provide invaluable emotional support.
In summary, while the journey from surgery to full recovery can be demanding, understanding what to expect at each stage helps ease anxiety and empowers patients to take an active role in their healing process. With proper care, support, and patience, patients can look forward to rediscovering their confidence and enjoying the results of their reconstructive journey.
Potential Risks and Complications to Consider
The DIEP flap procedure is widely recognized for its effective approach to breast reconstruction, primarily because it uses the patient’s own tissue to create a natural-looking breast. However, like any surgical intervention, it carries potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of before deciding to proceed. Understanding these can help patients make informed choices about their health and recovery strategies.
General Risks Associated with Surgery
As with most surgical procedures, patients undergoing the DIEP flap procedure may face common surgical risks, which include:
- Infection: Postoperative infections can occur, leading to prolonged recovery times or further interventions.
- Blood Clots: There is a risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often of the legs, which can migrate to the lungs (pulmonary embolism) and pose a serious health risk.
- Scarring: While the DIEP technique aims to minimize visible scars through strategic incisions, scarring is still an unavoidable outcome of surgery.
Flap-Specific Risks
In addition to general surgery-related risks, there are specific complications associated with flap procedures, particularly those involving tissue transfer:
- Flap Necrosis: This serious complication occurs when a portion of the transferred tissue does not receive adequate blood supply and starts to die. Signs of flap necrosis may include a change in the color of the breast area, swelling, or severe pain.
- Partial or Total Flap Failure: While rare, this can occur when the body rejects the new tissue or if there are complications that hinder blood flow. Affected patients may require additional surgical interventions.
- Asymmetry and Aesthetic Issues: It is possible for the reconstructed breast to not match the natural breast in shape, size, or positioning, leading to cosmetic dissatisfaction.
Additional Considerations
Patients should also be aware of other complications that could arise post-surgery:
- Seromas and Hematomas: Fluid accumulation (seromas) and blood collection (hematomas) can form at the surgical site, which may require drainage and could impede healing.
- Nerve Damage: Surgeons typically take precautions to preserve nerves during surgery; however, some patients may experience altered sensation or numbness in the breast and surrounding areas.
- Chronic Pain: Some patients report ongoing discomfort in the surgical area, impacting their quality of life post-surgery.
Table of Risks
| Risk | Description | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Post-surgical infection at incision sites | Low |
| Blood Clots | Formation of clots in veins due to immobility | Moderate |
| Scarring | Visible marks left post-surgery | High |
| Flap Necrosis | Decreased blood supply to transferred tissue | Rare |
| Partial/Total Failure | Tissue rejection or compromised blood flow | Rare |
| Asymmetry | Cosmetic mismatches between reconstructed and natural breasts | Moderate |
| Seromas/Hematomas | Fluid or blood accumulation post-surgery | Moderate |
| Nerve Damage | Altered sensations around the surgical site | Low |
| Chronic Pain | Ongoing discomfort in the surgical region | Moderate |
Mitigating Risks
Choosing an experienced plastic surgeon, adhering strictly to preoperative and postoperative instructions, and maintaining an honest dialogue with the healthcare team can significantly reduce the risks associated with the DIEP flap procedure. Thorough pre-surgical consultations can outline personalized strategies for minimizing complications.
Comparing DIEP Flap to Other Breast Reconstruction Options
When it comes to breast reconstruction, choosing the right procedure can be overwhelming. The DIEP flap procedure is one of several options available for reshaping the breast after mastectomy or injury. This section delves into how the DIEP flap stacks up against alternative methods, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
Types of Breast Reconstruction Options
Various techniques are available for breast reconstruction, mainly categorized into two groups: autologous (flap) reconstruction and implants. Below is a comparison of the DIEP flap procedure alongside some commonly used alternatives.
| Technique | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIEP Flap | Involves using skin and fat from the abdomen without sacrificing muscle. | – Natural look and feel – Reduced recovery time – Minimal abdominal muscle damage | – Longer surgery time – Requires donor site healing |
| TRAM Flap | Uses skin, fat, and muscle from the abdomen. | – Good tissue match – Can create natural contours | – Muscle removal can weaken the abdominal wall – Longer recovery |
| Latissimus Dorsi Flap | Involves harvesting tissue from the back. | – Smaller incisions – Adequate tissue for reconstruction | – Possible back weakness – Limited volume; may need implants for fullness |
| Breast Implants | Insertion of silicone or saline implants. | – Shorter recovery time – Can be placed in one surgery | – Risk of capsule formation – Less natural feel and appearance |
Advantages of DIEP Flap Over Other Methods
- Minimal Muscle Sacrifice: Unlike TRAM flap methods, the DIEP flap procedure does not involve removal of abdominal muscles, allowing for stronger core stability post-surgery.
- Natural Aesthetic: The use of autologous tissue typically leads to more natural-looking results, compared to implants that can sometimes appear artificial or feel less lifelike.
- Long-Term Durability: Since the DIEP flap uses your own tissue, it is less likely to need replacement or additional surgeries compared to implants, which may require future maintenance.
- Improved Healing: The recovery process may be smoother compared to TRAM flaps due to less manipulation of the abdominal muscles.
Disadvantages in Context
While the DIEP flap procedure offers many benefits, it’s also essential to consider its drawbacks. For patients who prioritize shorter recovery times, implant-based methods may be more appealing. Moreover, candidates must have sufficient abdominal tissue available for the flap, which may not be ideal for everyone.
Recent Trends in Breast Reconstruction
Recently, advances in surgical techniques and patient care have heightened the popularity of the DIEP flap procedure, especially among those seeking a more natural and long-lasting reconstruction option. Additionally, patient-centered care continues to promote education and informed decision-making processes, enabling individuals to explore their best options based on personal health and aesthetic goals.
Conclusion of Comparisons
In summary, choosing between the DIEP flap procedure and alternative breast reconstruction options involves weighing factors such as aesthetic outcomes, recovery time, and the potential for future surgeries. Each technique offers unique benefits tailored to individual needs and situations, highlighting the importance of thorough pre-operative consultations with a qualified surgical team to determine the best approach for each patient.
The Role of a Multidisciplinary Team in DIEP Flap Surgery
The successful execution of the diep flap procedure for breast reconstruction relies heavily on the collaboration of a multidisciplinary team. This intricate operation involves various healthcare professionals who provide comprehensive care before, during, and after the surgery. By harnessing a range of expertise, this team ensures that each patient receives personalized treatment tailored to their specific needs.
Key Team Members Involved
The multidisciplinary team typically includes the following professionals:
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Plastic Surgeon | Performs the diep flap procedure, focusing on the reconstruction of the breast. They ensure that the flap is designed and transferred appropriately for optimal aesthetic results. |
| General Surgeon | Assists with any underlying procedures, such as mastectomy, and collaborates with the plastic surgeon for a seamless surgical process. |
| Anesthesiologist | Responsible for administering anesthesia and monitoring the patient’s vital signs during the surgery, ensuring safety and comfort. |
| Nursing Staff | Provides pre-operative education, assists in post-anesthesia care, and monitors recovery to ensure the patient’s well-being throughout their hospital stay. |
| Oncologist | Works with cancer patients to determine if reconstruction is appropriate following cancer treatment and provides ongoing care if needed. |
| Physical Therapist | Develops a rehabilitation plan to restore mobility and strength after surgery, helping patients regain physical function. |
| Psychologist or Counselor | Offers emotional support and counseling services to help patients cope with the psychological aspects of breast reconstruction and recovery. |
| Nutritionist | Advises on dietary needs before and after surgery to promote healing and recovery, ensuring patients receive proper nutrition throughout the process. |
Importance of Team Collaboration
Collaboration among these professionals is essential for effective outcomes in DIEP flap surgery. Each member of the multidisciplinary team plays a crucial role, contributing their unique expertise. For example, while the plastic surgeon focuses on the reconstruction aspect, the general surgeon ensures that any cancer-related concerns are addressed. This merging of specialties creates a comprehensive plan that covers every aspect of the patient’s care.
Preoperative and Postoperative Stages
In the preoperative phase, this collaboration is evident in the thorough evaluations conducted by the team. Each member reviews the patient’s medical history and surgical needs, ensuring that all facets of care are addressed. This thorough assessment minimizes risks and prepares patients for the surgical journey ahead.
After the surgery, the multidisciplinary team continues to provide care. The nursing staff monitors recovery, the physical therapist implements a rehabilitation program, and the psychologist or counselor offers emotional support. This holistic approach contributes significantly to the patient’s overall well-being and satisfaction.
Conclusion
By embracing a multidisciplinary approach to the diep flap procedure, healthcare providers ensure that patients receive optimal care tailored to their unique situations. The collective expertise of this diverse team contributes significantly to achieving successful outcomes, alleviating the challenges associated with breast reconstruction, and enhancing the overall healing process. With their combined knowledge and support, patients can feel confident in each step they take towards recovery.
Post-Operative Care and Support for Patients
Undergoing a DIEP flap procedure is a significant step towards breast reconstruction, and the journey continues even after the surgery is complete. Post-operative care is critical for ensuring a successful recovery and achieving optimal aesthetic outcomes. This section will explore the essential elements of post-operative care and support necessary for patients recovering from a DIEP flap procedure.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
- Hospital Stay: Following the surgery, patients typically remain in the hospital for 2 to 5 days. During this time, medical staff will monitor vital signs, pain levels, and the condition of both the donor and the recipient sites.
- Pain Management: Pain is an expected part of recovery. Patients may be prescribed medications to manage discomfort effectively. It’s essential to communicate openly with healthcare providers about pain levels and side effects of any medication.
- Monitoring the Flap: One of the primary concerns after surgery is ensuring that the blood flow to the flap is adequate. Clinicians will assess circulation through observations and possibly using Doppler ultrasound to listen to the blood flow in the reconstructed area.
Home Care Guidelines
Once discharged, certain care protocols must be followed to promote healing at home:
- Wound Care: Patients should keep the surgical sites clean and dry to prevent infections. It’s important to follow the surgeon’s instructions on how to care for incisions, including when to change dressings and signs of possible infection (such as increased redness or discharge).
- Activity Restrictions: Limiting physical activity is crucial during the recovery period. Patients are usually advised to avoid lifting heavy objects, engaging in strenuous activities, or exercising for several weeks.
- Hygiene Practices: Gentle hygiene practices should be employed, especially around surgical sites. Patients should avoid swimming pools and hot tubs until fully healed to reduce infection risk.
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration play vital roles in recovery.
| Nutrients | Importance | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Essential for tissue repair and healing | Lean meats, fish, beans |
| Vitamins (A & C) | Supports skin health and immune function | Citrus fruits, leafy greens |
| Zinc | Accelerates wound healing | Nuts, whole grains |
| Hydration | Aids bodily functions and promotes recovery | Water, herbal teas |
Emotional Support
Emotional and psychological well-being is just as vital as physical healing:
- Support Networks: Encouragement from friends and family can significantly ease the recovery process. Open discussions about experiences and feelings can help patients feel understood and supported.
- Counseling Services: Some patients may benefit from professional counseling or support groups to cope with the emotional and psychological impacts of breast reconstruction.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up visits are crucial for monitoring the progress of recovery and addressing any concerns that may arise.
- Frequency of Visits: Patients usually have follow-ups scheduled one week after discharge, then at intervals of one to three months. These appointments allow the surgeon to assess healing, address questions, and offer additional guidance.
- Long-term Monitoring: Long-term follow-up is essential to evaluate the aesthetics of the breast reconstruction and the overall well-being of the patient.
In summary, post-operative care and support for patients after a DIEP flap procedure are fundamental components that significantly influence recovery and satisfaction with the reconstruction outcome. By adhering to medical advice, maintaining communication with healthcare providers, and seeking emotional support, patients can navigate this vital period of healing most effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions About the DIEP Flap Procedure
As you explore options in breast reconstruction, numerous questions may arise regarding the intricacies of the DIEP flap procedure. This method, which utilizes tissue from the abdomen to reconstruct the breast, often prompts inquiries about the process, recovery, and overall efficacy. Below are some frequently asked questions that can aid your understanding of this procedure.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the expected recovery time after surgery? | Recovery typically varies per individual, but most patients can expect to return to light activities within 2-4 weeks. Complete healing may take several months, with full results visible after about a year. |
| Are results from the DIEP flap procedure permanent? | Yes, the reconstructed breast can maintain its form and feel over time. However, factors such as aging and physiological changes can still affect the appearance, similar to natural breasts. |
| How does the surgery impact abdominal strength? | While the procedure removes tissue and fat from the abdominal area, most patients do not experience significant loss of abdominal strength. Your surgeon will provide post-operative guidelines to support recovery. |
| Is it possible to have the procedure after previous breast surgeries? | Yes, many women with prior surgeries, such as lumpectomies or mastectomies, can still qualify for this reconstruction technique. A thorough examination by a specialized surgeon will determine the feasibility. |
| Will the surgery leave scars? | Yes, scarring will occur both at the breast reconstruction site and the donor site on the abdomen. Surgeons typically use techniques to minimize scarring, and over time, these scars usually fade. |
| Is it safe to undergo the procedure if I smoke? | Smoking can complicate the surgery and recovery process. It is highly recommended to quit smoking several weeks prior to the operation and refrain from it during the healing process to promote optimal outcomes. |
| What kind of anesthesia is used during surgery? | Patients typically receive general anesthesia during this procedure. This ensures comfort and allows the surgeon to perform the operation safely. |
| How do I choose a surgeon for this procedure? | Selecting a surgeon with specialized training and expertise in breast reconstruction is crucial. Look for board certification, patient reviews, and a portfolio of previous work to assist in your decision. |
| Can this procedure be done for those who are overweight? | Being overweight isn’t an automatic disqualifier; however, it can affect surgical outcomes. A discussion with your surgeon can clarify whether this method is appropriate given your health and BMI. |
| What support systems are available post-surgery? | After the surgical process, patients can access numerous support resources, including physical therapy, counseling services, and support groups for those undergoing breast reconstruction. |
As you gather more information, consider reaching out to your healthcare provider for personalized answers. Understanding these questions can empower you to make informed decisions about your journey toward breast reconstruction. Remember that a supportive environment, combined with accurate knowledge, plays a crucial role in the overall experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the DIEP flap procedure for breast reconstruction?
The DIEP (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator) flap procedure is a type of breast reconstruction surgery that utilizes the patient’s own tissue to create a new breast after mastectomy. This innovative technique involves taking skin and fat from the lower abdomen while preserving the abdominal muscles, thereby minimizing recovery time and complications. The tissue is then carefully shaped and attached to the chest area to recreate the natural appearance of a breast. This method not only provides a more aesthetically pleasing result but also maintains the integrity of the abdomen.
How is the DIEP flap procedure different from other breast reconstruction methods?
The DIEP flap procedure is distinct from other breast reconstruction options, such as implants or other types of flap surgeries, mainly due to its use of the patient’s own tissue without sacrificing muscle. Unlike the TRAM flap, which involves moving muscle from the abdomen, the DIEP flap preserves all abdominal muscles, leading to fewer complications, less pain, and a quicker recovery. Additionally, because it uses natural tissue, the DIEP flap can provide a more realistic feel and appearance compared to synthetic implants.
What is the recovery process like after a DIEP flap procedure?
Recovery after a DIEP flap procedure typically involves a hospital stay of 3 to 5 days, followed by several weeks of at-home recovery. Patients are advised to refrain from lifting heavy objects and engaging in strenuous activities for at least 6 to 8 weeks. Though most patients can return to light activities within a few weeks, full recovery may take longer. The area from which tissue was harvested may have some discomfort, swelling, or bruising, but these effects generally subside within a few weeks. Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with the DIEP flap procedure?
As with any surgical procedure, the DIEP flap surgery carries potential risks and complications, though they are generally low. These may include infection, bleeding, delayed wound healing, and problems with the flap, such as loss of blood supply, which could lead to flap failure. Some patients might also experience changes in sensation or scarring in both the breast and abdominal areas. It is crucial for patients to discuss these risks thoroughly with their surgeon prior to the procedure to ensure they make an informed decision.
Who is an ideal candidate for the DIEP flap procedure?
The ideal candidate for the DIEP flap procedure is typically a woman who has undergone a mastectomy and seeks natural-looking breast reconstruction using her own tissue. Candidates should have sufficient abdominal tissue to create a breast and have no significant medical conditions that could impair healing, such as uncontrolled diabetes or vascular disease. Additional considerations include the patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and personal preferences. An in-depth consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon specializing in breast reconstruction is essential to determine candidacy.